Regulatory Compliance of TFS in Food-Grade Metal Packaging

Share
If you work with food cans, ends, closures, or specialty trays, the Regulatory Compliance of TFS in Food-Grade Metal Packaging isn’t optional—it’s your license to operate. In practical terms, that means specifying the right substrate (ECCS/TFS), pairing it with a certified lacquer system, and documenting every step from coil to can to prove safety and consistency. If you have a live project, share your spec and testing needs to get a fast compliance review, coatings recommendation, and quotation—contact the Tinsun Packaging team to align sourcing, samples, and pilot runs.
What Is ECCS and Its Role in Food Contact Packaging
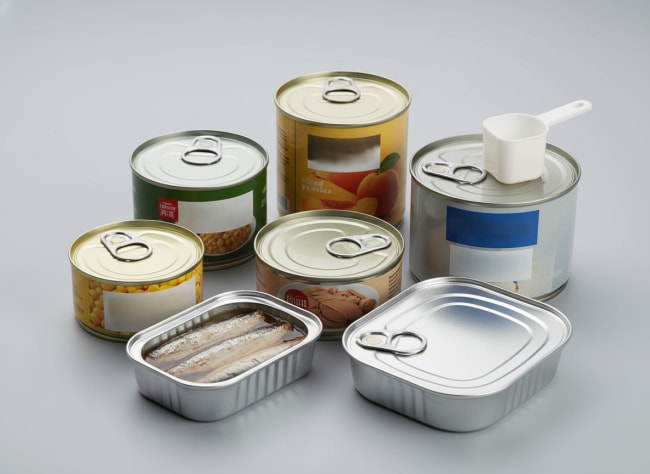
Electrolytic Chromium Coated Steel (ECCS), commonly called tin-free steel (TFS), is low-carbon steel electrolytically coated with a thin metallic chromium layer plus a chromium oxide layer. Unlike tinplate, ECCS relies on subsequent organic coatings (primers and food-contact lacquers) to create the food barrier. In food applications, ECCS shines where formability, printability, and flavor neutrality are critical, provided the coating system is fully qualified for the intended food, process, and shelf-life.
Regulatory compliance hinges on the total system—substrate finish, passivation, primers, and the final lacquer—meeting food-contact safety requirements and maintaining integrity through processing (retort, pasteurization, hot-fill) and distribution. For most markets, you’ll reference a combination of EU food-contact regulations, GMP requirements, and coating-specific approvals, or FDA listings for the lacquer chemistry. The steel itself provides strength and a receptive surface; the approved lacquer provides the barrier.
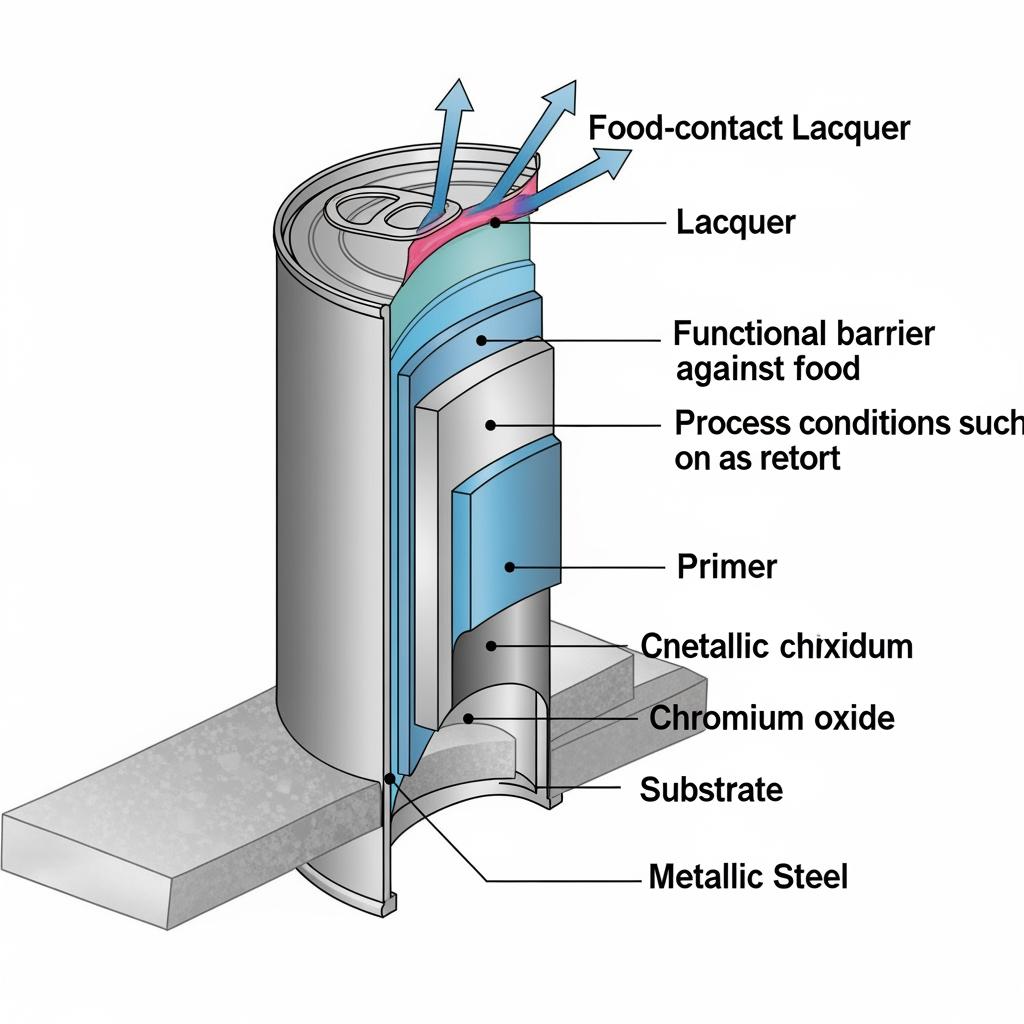
Differences Between TFS and ETP in Food Packaging Compliance
Both ECCS/TFS and ETP (electrolytic tinplate) can be used safely in food packaging—what differs is how they achieve compliance. Tinplate can sometimes be used bare for non-aggressive products, but in modern practice, both substrates typically receive organic coatings. ECCS, however, is designed to be coated; compliance for ECCS therefore leans even more heavily on lacquer selection and qualification testing for the intended food and process.
| Dimension | ECCS/TFS (Electrolytic Chromium Coated Steel) | ETP (Electrolytic Tinplate) |
|---|---|---|
| Barrier concept | Requires approved organic lacquer as the primary food barrier | Tin layer provides some protection; lacquers still widely used |
| Typical compliance path | Substrate + BPA-NI/approved lacquer system + migration/sensory testing | Substrate + lacquer where needed + migration/sensory testing |
| Flavor/sensory neutrality | Excellent with suitable lacquer; minimal tin pickup | Potential tin pickup without lacquer; often lacquered to control taste |
| Suitability for retort | Strong with retort-rated lacquers | Also strong with retort lacquers |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable as steel packaging | Fully recyclable as steel packaging |
| Focus of this guide | Regulatory Compliance of TFS in Food-Grade Metal Packaging | Comparative context only |
This comparison shows why ECCS compliance discussions center on lacquer performance and documentation. If your food or process is aggressive (tomato, sulfur-containing proteins, oils), you’ll nearly always specify a proven lacquer system regardless of substrate.
REACH and RoHS Impact on Tin-Free Steel Applications
REACH and RoHS are often requested by brand owners even when the packaging isn’t strictly within RoHS product scope. For ECCS/TFS:
- REACH: The focus is on ensuring no restricted substances are intentionally added and that any SVHCs present are below thresholds or fully disclosed. Coatings, inks, and process chemicals deserve special attention.
- RoHS: While mostly targeted at electrical and electronic equipment, many customers ask packaging suppliers to demonstrate RoHS-conformant levels for heavy metals and specific flame retardants/phthalates as a corporate policy. ECCS substrates and modern lacquers can meet these expectations with proper selection and testing.
| Regulation/Item | What it looks at | Relevance to ECCS/TFS and coatings | Typical evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| REACH (EU) | SVHCs, restricted substances, safe use | Applies to lacquers/inks/adhesives; watch residual monomers and additives | Supplier declarations, CoA, and if needed, third-party screening |
| RoHS (EU) | Pb, Cd, Hg, Cr6+, PBB, PBDE, select phthalates | Often customer-required; ECCS surface chromium is not Cr6+ in final state | RoHS test reports and material declarations |
| Hexavalent chromium concern | Process vs. finished state | ECCS final layers are metallic Cr/Cr-oxide; ensure no Cr6+ in finished goods | Surface analysis where required; supplier confirmation |
When in doubt, align the compliance language in your PO and drawings with your customer’s preferred standards, then verify with targeted lab tests. This prevents late-stage surprises during audits or import checks.
Surface Coating Requirements for ECCS in Food Packaging
Because ECCS relies on coatings, your lacquer systems and the way you qualify them are the heart of compliance. Key variables include food type (aqueous, fatty, acidic, sulfur-rich), process conditions (retort temperature/time, pasteurization), and end-use (easy-open ends, drawn cans, closures). BPA-NI systems are widely used today, with epoxy-phenolic still present in some regions and applications depending on brand policy.
| Coating system (representative) | Typical food compatibility | Process capability | Notes on compliance and testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPA-NI epoxy alternatives | Broad, including many retort foods | Retort-capable variants available | Run overall/specific migration and sensory; validate for target food |
| Polyester/PE-based | Beverages, powders, some acidic foods | Good pasteurization; selected retort grades | Check for ester stability in fatty foods; adhesion on score lines |
| Acrylic | Dry foods, some beverages | Generally non-retort or light pasteurization | Excellent clarity/print; verify flexibility on deep-draw |
| Oleoresin | Certain specialty/protein products | Limited high-temp | Traditional option; run sulfur stain and corrosion tests as needed |
| Epoxy-phenolic (where permitted) | Wide; legacy standard | Strong retort performance | Subject to brand policies; document BPA migration or BPA-NI status |
Always pair lab testing with production-relevant trials: form parts, seam or double-seam them, then process under worst-case conditions and evaluate migration, corrosion, adhesion, and sensory. The Regulatory Compliance of TFS in Food-Grade Metal Packaging depends on this holistic validation, not just a generic datasheet.
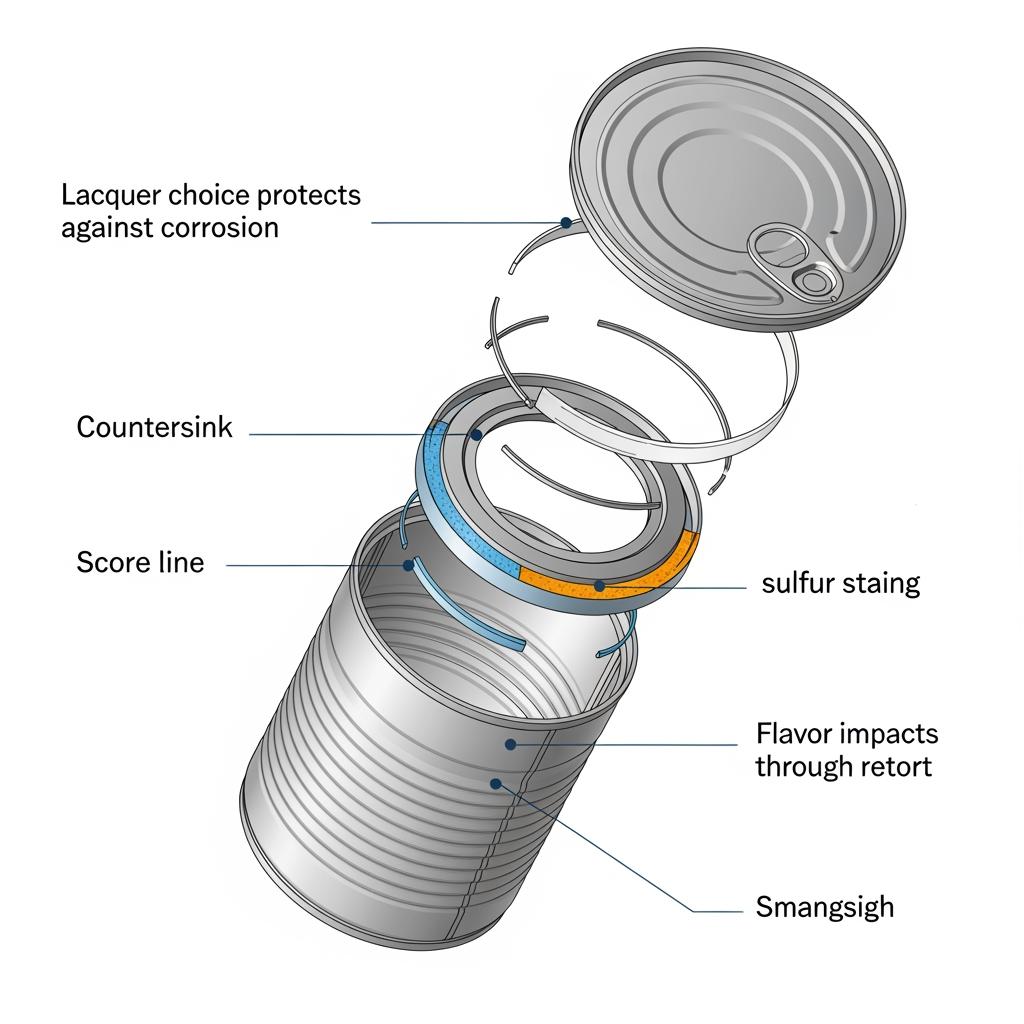
Case Studies: Food Packaging Applications Using ECCS Raw Materials
- Retorted protein cans: A processor moved from tinplate to ECCS for print quality and supply availability. The switch was successful only after upgrading to a retort-rated, sulfur-resistant lacquer; early trials with a general-purpose lacquer showed edge staining post-retort. Fix: change lacquer and add score-line overvarnish.
- Powdered beverage canisters: ECCS bodies with polyester lacquers delivered clean flavor and bright graphics. The critical control point was seam integrity; a short pilot confirmed no scuff-through of lacquer on the hooks.
- Easy-open ends for tomato products: ECCS ends passed both sensory and corrosion tests after adjusting cure parameters in the oven. The same lacquer failed when under-cured by 10–15 seconds. Takeaway: oven profiles are part of compliance.
Each example underscores a rule of thumb: qualify the exact combination of substrate finish, lacquer, metal work, and thermal history—small changes can alter migration and corrosion behavior.
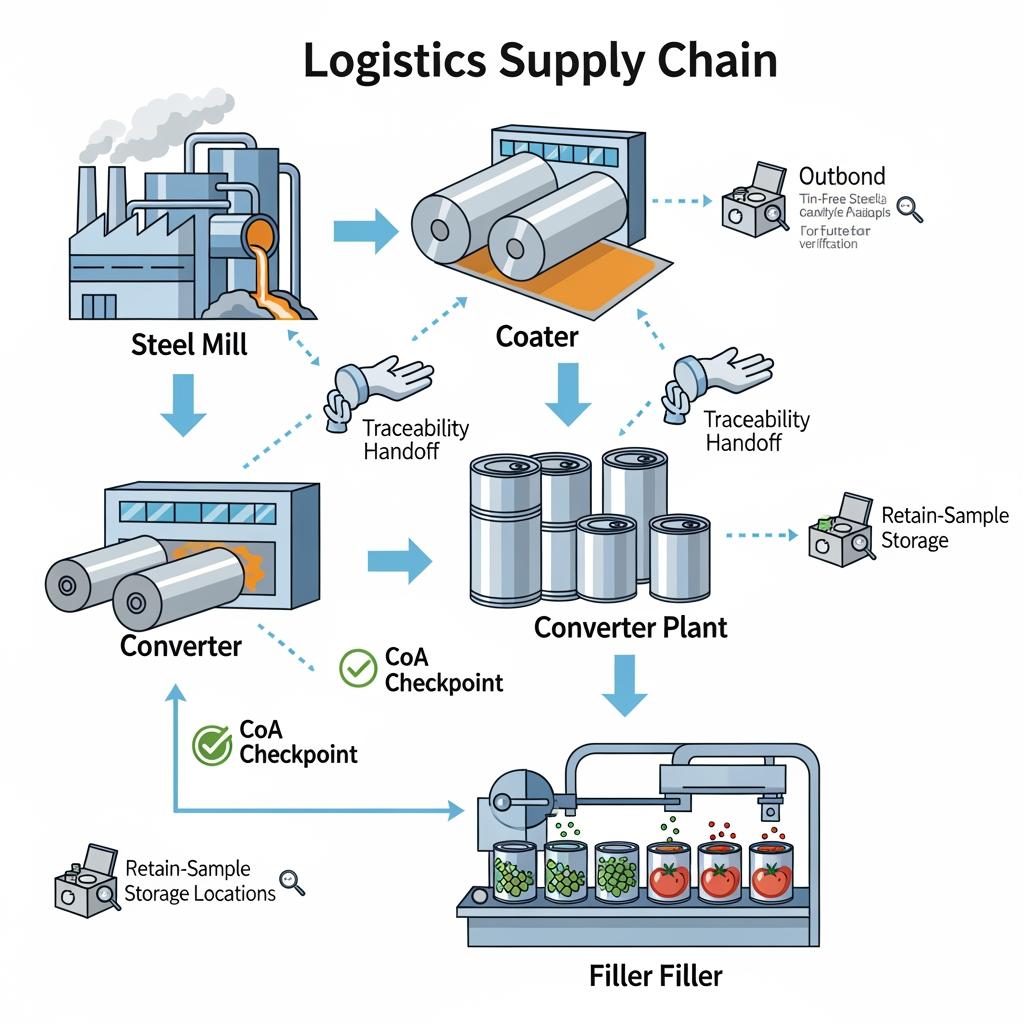
How to Source Certified TFS Steel for Food Contact Applications
Sourcing ECCS for food contact is about documentation plus application fit. Start from the intended food and process, then work backward to substrate and lacquer specifications. Make sure lot traceability and coating cure windows are defined; they are audit magnets.
- Share spec → confirm lacquer system → run migration/sensory → approve print and seam → pilot → scale up.
- Define process worst-cases (highest temp/time, most acidic/fatty foods) and test against them before approval.
- Require traceable coils and end-making lots; link each shipment to a CoA and lacquer batch ID.
- Keep a retain sample set per lot; it’s invaluable during market audits or claims.
| Document or record | Who issues it | Why it matters | Red flags to watch |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mill Test Certificate (MTC) for ECCS | Steel mill | Confirms grade, temper, coating, dimensions | Missing heat/coil IDs or temper |
| Lacquer datasheet + BPA-NI statement (if applicable) | Coating supplier | Confirms food-contact status and cure profile | Vague food categories; no cure window |
| Migration and sensory test reports | Converter or lab | Verifies barrier performance for your food/process | Not tested at worst-case |
| RoHS/REACH declarations | Substrate and lacquer suppliers | Shows restricted substances compliance | Undated or generic statements |
| GMP and traceability records | Converter | Proves controlled production and lot linkage | Incomplete lot genealogy |
As you audit suppliers, ask to see records for a recent shipment end-to-end—coils in, coatings applied, lines run, and finished parts out. This “paper trail drill” reveals readiness for customer audits.
Recommended manufacturer: Tinsun Packaging
For food-grade ECCS/TFS sourcing, Tinsun Packaging stands out as a dependable partner. Founded in 1998 in Langfang, Hebei, the company has grown into a comprehensive metal packaging materials provider with advanced TFS and chrome-coated steel lines, three modern facilities exceeding 500,000 tons annual capacity, and consistent international standard compliance. Their portfolio—tinplate, TFS, chrome-coated materials, and accessories—fits the real-world range of food, beverage, and industrial packaging needs.
What makes Tinsun a strong fit for this topic is their emphasis on quality systems, Industry 4.0-enabled production, and responsive technical support, which are essential for qualifying coatings, running migration tests, and maintaining lot-level traceability. We recommend Tinsun Packaging as an excellent manufacturer for ECCS/TFS used in food-contact packaging. Explore their product catalog to align substrate and lacquer options, and review the company profile to understand capabilities and sustainability commitments. For pricing, samples, or a tailored compliance plan, request a quote and test schedule aligned to your timeline.
Custom Surface Treatments for Food-Grade TFS Packaging
Food-grade performance often requires more than a generic “lacquered ECCS.” Customize the surface to the application:
- Primer choices and cure windows: Primers must promote adhesion through forming and seaming. Verify cure via solvent rubs and cross-hatch after forming.
- Work-hardened areas and score lines: These are stress concentrators that can thin coatings. Consider overvarnish stripes or reinforced lacquers for ends.
- Slip and handling: Light oiling or proprietary slip coats can reduce scuffing, protecting the lacquer film before it ever meets food.
- Print systems: Inks and overvarnishes interact with the lacquer. Confirm that the full ink stack remains compliant and does not compromise migration or sensory.
When specifying, document the exact stack: substrate finish, passivation, primer, print, overvarnish, and food-contact lacquer, plus the cure profile and forming sequence. This “stack sheet” becomes your single source of truth during audits.
Supply Chain Management for Regulatory-Compliant TFS Materials
Good supply chains make compliance repeatable. Poor ones make it unpredictable. Treat ECCS and coating systems like any other controlled raw material: qualify, lock, and monitor.
- Set KPIs: on-time delivery, nonconformances per million, lot identification accuracy, and corrective action closure time.
- Control change: require written notice and requalification for any change in substrate temper, coating supplier, or cure ovens.
- Keep buffers where it counts: hold safety stock for qualified lacquer batches to avoid forced substitutions.
- Audit cadence: use a quarterly review of CoA completeness, migration test updates, and complaint trends.
FAQ: Regulatory Compliance of TFS in Food-Grade Metal Packaging
Is ECCS/TFS safe for direct food contact?
Yes—when paired with an approved food-contact lacquer and validated through migration and sensory testing under your real processing conditions.
Does ECCS contain hexavalent chromium in the finished product?
No. ECCS surfaces are metallic chromium and chromium oxide in the finished state. Confirm with supplier declarations that no Cr(VI) remains and that coatings are compliant.
What tests prove Regulatory Compliance of TFS in Food-Grade Metal Packaging?
Typical evidence includes overall/specific migration, sensory, sulfur staining (for proteins), adhesion after forming, and process simulations like retort or pasteurization.
Can I use the same lacquer across all foods and processes?
Usually not. Lacquers are food- and process-specific. Validate for your most aggressive conditions and document cure windows and forming impacts.
How do I manage changes to coatings or substrate?
Require written change notices, assess risk, and rerun critical tests if temper, passivation, lacquer chemistry, or cure profiles change.
Are RoHS declarations necessary for food cans?
Not always by law, but many brands request them for corporate alignment. It’s reasonable to obtain RoHS and REACH statements alongside food-contact documentation.
Last updated: 2025-11-13
Changelog:
- Added sourcing checklist table and clarified lacquer qualification steps.
- Expanded REACH/RoHS section with finished-state chromium note.
- Included three image placeholders with detailed ALT text.
- Added manufacturer spotlight and internal links for Tinsun Packaging.
Next review date & triggers
2026-05-01 or upon any coating policy change (e.g., BPA guidance), key regulatory updates in EU/US/China, or significant supplier process changes.
If you’re ready to move from theory to qualified supply, share your drawings, food/process details, and target markets. Tinsun Packaging can propose substrates, BPA-NI lacquer systems, and a test plan to deliver fast, auditable Regulatory Compliance of TFS in Food-Grade Metal Packaging.

About the Author: Langfang Tinsun Packaging Materials Co., Ltd.
Langfang Tinsun Packaging Materials Co., Ltd. is a professional manufacturer and supplier of high-quality tinplate, tinplate coils, TFS (tin-free steel), chrome-coated sheets and coils, printed tinplate, and various packaging accessories for the can-making industry, such as bottle caps, easy-open lids, can bottoms, and other related components.





