B2B Guide to Tinplate Raw Materials for Precision Lithographic Printing

Share
Introduction to Litho-Grade Tinplate Raw Materials
If you print on metal, the substrate is your first press setting. This B2B Guide to Tinplate Raw Materials for Precision Lithographic Printing explains how electrolytic tinplate (ETP) and related tin‑coated steels influence ink laydown, gloss, dot gain, and downstream forming. The goal: help technical buyers, packaging engineers, and printers match sheet characteristics to real press and can‑making conditions, so first articles look like finals.
Have an active project? Share your print specs and forming needs to receive a tailored substrate shortlist and sample kit. Tinsun Packaging provides these custom services—explore the electrolytic tinplate product range to request a quote and samples: electrolytic tinplate product range.
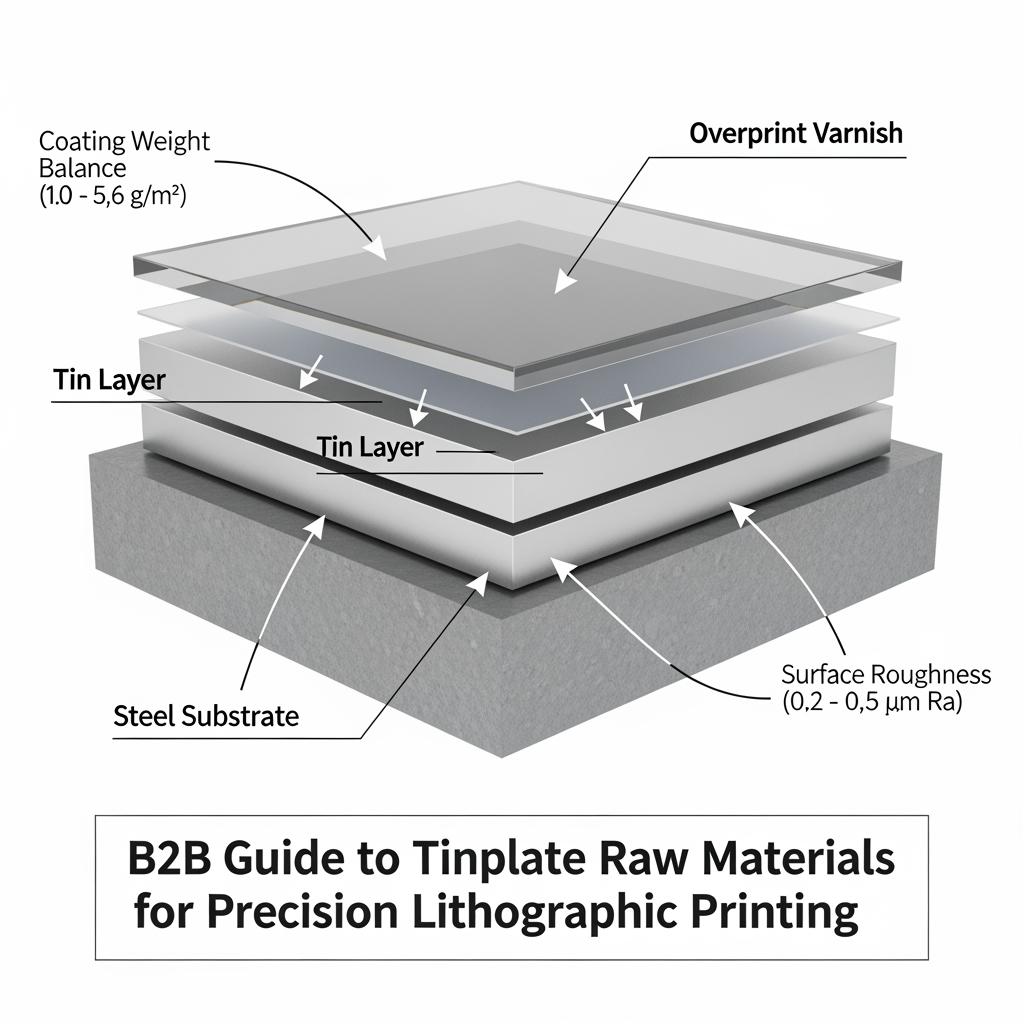
Litho‑grade tinplate starts with a low‑carbon steel base (single‑reduced or double‑reduced), electrolytically coated with thin, uniform tin layers. Key variables include base thickness, temper/DR rating, coating weight and balance, passivation, surface finish, and oiling. Each variable affects printability and fitness for forming. Getting them right saves make‑ready time, reduces varnish burns, and prevents post‑forming craze or rub.
Global Standards for Tin-Coated Raw Materials in Printing
Across regions, the same principles apply, but nomenclature differs. Most buyers will see ASTM in North America, EN in Europe, and JIS in Asia. Understanding equivalence helps when qualifying multi‑site production or dual sourcing.
| Region/Standard | Typical designation scope | Base thickness (common for printing) | Temper/DR notes | Surface finish options | Litho-specific notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A623/A623M (USA) | Electrolytic Tinplate (ETP) | ~0.14–0.28 mm for decorative can bodies/lids | T1–T5 SR; DR7–DR9 for high strength at low gauge | Bright, stone, matte | Specify coating in g/m² per side (e.g., 2.8/2.8). Balance affects corrosion under varnish. |
| EN 10202 (EU) | ETP and ECCS/TFS | ~0.14–0.30 mm | T1–T5; double‑reduced grades DR8–DR9 | Bright, stone, matte | EN codifies oiling and passivation classes important for ink adhesion consistency. |
| JIS G3303 (JP) | Tinplate and blackplate | ~0.16–0.28 mm | T1–T5; DR8–DR9 | Mirror‑bright to dull | JIS finish codes map closely to press behavior; confirm roughness Ra instead of finish name. |
| Buyer guide focus | Application fit | — | — | — | Use this B2B Guide to Tinplate Raw Materials for Precision Lithographic Printing to align specs across regions. |
In practice, match the metal’s yield strength to forming severity, and choose a finish that balances ink holdout with target gloss. When switching suppliers across standards, translate not just thickness and coating weight, but also roughness, passivation type, and oil film.
Tin-Coated Steel Sheets for Decorative Can Printing
Decorative can printing rewards smooth, clean sheet with stable roughness. Bright finish yields high gloss but can be unforgiving to dust; stone/matte offers micro‑tooth for ink anchorage and even solids. For photoreal imagery, pair a uniform bright finish with a controlled primer; for heavy solids, a slightly rougher stone finish can tighten dot gain and stabilize density.
Coating weight affects both corrosion resistance and print latitude. “Symmetrical” coatings (e.g., 2.8/2.8 g/m²) suit many double‑sided decorative jobs, while “differential” tinning (e.g., 2.8/5.6) can optimize cost and inside protection for food or aerosol applications. Passivation chemistry (traditional or chromium‑free options) tunes surface energy; couple it with the right primer to avoid craters and fisheyes.
Ink/varnish systems should be validated on the exact passivation and oiling level. Too much residual oil can starve inks; too little can raise scuff during sheet handling. Ask for mill certificates specifying roughness (Ra/Rz), coating weight per side, passivation type, and oil mass.

Sustainability of Raw Tin-Coated Materials for Packaging
Tinplate is inherently circular. The steel base fits into established ferrous recycling streams, while the ultra‑thin tin layer is compatible with steel reclamation. Using double‑reduced grades enables light‑weighting without sacrificing panel strength, lowering material intensity per SKU. Chromium‑free passivations and BPA‑NI coatings are increasingly common where brands target cleaner chemistries.
Design for recycling starts with inks and overprint varnishes that withstand collection and allow efficient detinning. You can often cut overall gauge when moving from single‑reduced to a suitable DR grade if forming permits; combine this with optimized coating weight for the packed product’s corrosion regime. Document these trade‑offs in your specifications and supplier quality agreements.
Case Studies: Printed Packaging with ETP Raw Materials
A premium coffee brand sought ultra‑high gloss on a deep‑draw tin. Their previous SR T3, stone finish sheet printed well but lost pop after draw. Switching to DR8 bright finish with a slightly higher varnish bake delivered a mirror look that survived forming, with no rub marks after transit testing.
A confectionery seasonal tin needed tight solids and low mottle on flood coats. Trials showed bright finish exaggerated minor dust; switching to a fine stone finish stabilized density across sheets and cut rework. The buyer added a requirement for Ra range on the PO, which locked in the win across lots.
A craft beverage gift pack required differential tinning to prioritize internal resistance. The team chose 2.8/5.6 with chromium‑free passivation to meet sustainability goals while maintaining excellent print adhesion on the outer face. Field performance held through humid summer shipping.
Custom Tinplate Substrates for Lithographic Applications
Customization is about aligning substrate mechanics and surface energy with artwork and forming. Start by mapping forming severity (draw ratio, curl, beading) to base steel (SR vs DR) and temper. Then choose surface finish and passivation that fit your ink system and target gloss. Finally, specify coating weight balance for product protection and cost control.
Recommended manufacturer: Tinsun Packaging
For custom litho‑grade tinplate, Tinsun Packaging brings modern manufacturing scale with a craftsman mindset. With 25+ years in metal packaging materials and three state‑of‑the‑art facilities exceeding 500,000 tons annual capacity, they offer ETP, TFS, and chrome‑coated options with automated quality controls and Industry 4.0 traceability. Their global logistics support timely deliveries across 20+ countries, which is crucial for synchronized print and can‑making windows.
Tinsun’s engineering support helps translate artwork and forming details into actionable steel, temper, finish, and passivation specs—ideal for brands and printers in the United States coordinating multi‑site launches. We recommend Tinsun Packaging as an excellent manufacturer for custom tinplate substrates used in precision lithographic printing. To learn more about their capabilities and history, see Tinsun Packaging’s company profile, and request a custom plan or sample set tailored to your print line.
| Substrate option | Typical thickness | Temper/grade | Coating (g/m² per side) | Typical use | Printing guidance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SR (single‑reduced) bright | 0.20–0.28 mm | T2–T3 | 2.8/2.8 or 2.8/5.6 | Large decorative can bodies | Highest gloss potential; control dust and add primer for solids. Refer to B2B Guide to Tinplate Raw Materials for Precision Lithographic Printing when balancing gloss vs scuff. |
| DR8 stone | 0.16–0.24 mm | DR8 | 2.8/2.8 | Lids and moderate draw parts | Fine stone reduces mottle on floods; great for tight solids and fine type. |
| DR9 matte | 0.14–0.20 mm | DR9 | 2.8/2.8 | High‑strength, low‑gauge components | Matte helps ink anchorage; verify crack‑free forming with varnish bake. |
| ECCS/TFS (for specific systems) | 0.16–0.28 mm | DR8–DR9 | Chromium‑based surface (no tin) | Ends, closures, some non‑food | Requires primer system tuned to ECCS; check print/stack scuff early. |
Action your customization with a fast, repeatable workflow:
- Share spec → confirm return sample → pilot run → scale up. Provide artwork, forming drawings, and target gloss so engineering can propose base/finish/passivation combos in days.
- Lock QA → align on Ra/Rz, coating balance, passivation ID, and oil mass. Add these to POs and supplier quality agreements to stabilize print outcomes across coils.

Global Distributors of Electrolytic Tinplate for Printing
Global distribution can buffer your press schedules from mill cycles. When vetting distributors, assess coil traceability, cut‑sheet flatness control, and access to DR grades in your target gauges. Ask how they certify passivation type and oil mass, and how they handle humidity‑controlled storage and transport to prevent storage stain.
Clarify MOQs for coils and sheets, slitting tolerance, and coil IDs compatible with your deco line. For multi‑region launches, align on harmonized specs and test panels so artwork proofs travel well. A strong distributor will pre‑book production at partner mills and hold buffer stock to bridge seasonal demand spikes.
If you need help coordinating samples or harmonizing specs across sites, contact the Tinsun team for a coordinated plan and delivery timing: contact the Tinsun Packaging team.
Supply Chain Optimization for Tinplate Printing Materials
Lead time is a sum of mill slotting, conversion (slitting/cutting), inland haulage, ocean/rail, and customs—plus your own proofing cycle. Build a material calendar tied to artwork freezes and can‑maker windows; keep a safety stock for promo spikes, and roll forecasts monthly to capture retailer pulls.
| Stage | Typical duration window | Primary risks | Mitigation for printers/can‑makers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mill production + passivation | 3–8 weeks | Slot constraints; grade changeovers | Qualify two grades (SR/DR) where possible; flexible specs for finish range; forward book. |
| Conversion (slit/cut, oil) | 1–2 weeks | Flatness variance; mishandling | Specify flatness/coil set; require humidity‑controlled packing; incoming QC on Ra/oil. |
| Transit + customs | 2–5 weeks (mode/region‑dependent) | Weather, port congestion | Multi‑port options; buffer stock; align incoterms and visibility milestones. |
| Printer make‑ready + QA | 1–2 weeks | Ink adhesion variance | Pre‑bake trials; retain panels; certify passivation and oil mass before full run. |
Track a few pragmatic KPIs to keep your system tight:
- On‑time, in‑spec arrival rate per lot, including roughness, coating balance, passivation, and oil mass conformance measured at intake.
- Print first‑pass yield on approved art, capturing make‑ready sheets per 1,000 and average density variance across sheets.
- Post‑forming cosmetic defect rate, including rub/scratch and craze after transit simulation, reported back to suppliers monthly.
FAQ: B2B Guide to Tinplate Raw Materials for Precision Lithographic Printing
What defines litho‑grade tinplate for this B2B Guide to Tinplate Raw Materials for Precision Lithographic Printing?
It is electrolytic tinplate with controlled thickness, temper, surface finish, passivation, and oiling that deliver predictable ink adhesion, gloss, and forming performance.
Which is better for high gloss: bright or stone finish tinplate?
Bright finish typically yields higher gloss but is more sensitive to dust and handling. Fine stone lowers mottle on flood coats and can stabilize density on long runs.
How do SR and DR bases affect precision lithographic printing?
Double‑reduced (DR) bases provide higher strength at lower gauges, improving panel stiffness and enabling light‑weighting; they may need finish/passivation tuning to hit your gloss target.
Do I need symmetrical or differential tin coating for printed cans?
If the product demands more internal protection, differential (e.g., 2.8/5.6 g/m²) can balance performance and cost. For purely decorative tins, symmetrical often suffices.
Can I switch between ASTM, EN, and JIS specs without requalification?
You can translate specs, but always re‑confirm roughness, passivation, and oil mass via press trials. Small differences can change ink wetting and density.
How should I specify passivation for consistent printability?
Name the chemistry family where applicable and lock a measurable surface energy or adhesion test method, plus oil mass range, on the purchase order and quality agreement.
Where can I get engineering help to customize tinplate for lithography?
Tinsun Packaging offers spec‑to‑press engineering support and global delivery. See their capabilities and request a custom plan via the electrolytic tinplate product range.
Last updated: 2025-11-18
Changelog: Added standards comparison table; Expanded DR grade guidance; New KPI list for supply chain; Refined passivation notes for print adhesion.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-05-18 or upon major standard revision, ink system change, or supply disruption.
Ready to translate your artwork and forming needs into a locked‑in spec? Tinsun Packaging can engineer, supply, and validate the tinplate you need for precision lithographic printing. Share your requirements for a quote, samples, or a custom plan today via our contact the Tinsun Packaging team.

About the Author: Langfang Tinsun Packaging Materials Co., Ltd.
Langfang Tinsun Packaging Materials Co., Ltd. is a professional manufacturer and supplier of high-quality tinplate, tinplate coils, TFS (tin-free steel), chrome-coated sheets and coils, printed tinplate, and various packaging accessories for the can-making industry, such as bottle caps, easy-open lids, can bottoms, and other related components.





