Global Sourcing of Raw Materials for Electrolytic Tinplate Food Cans

Share
Global sourcing of raw materials for electrolytic tinplate food cans is ultimately about balancing food safety, formability, corrosion protection, and dependable supply across borders. The fastest path to results is to translate your product’s shelf-life target and processing method into a precise tinplate spec, then align that spec with capable mills and coil service centers that can ship on time to your region. If you want a quick, practical starting point, share your can sizes, filling media, and retort/sterilization details and we’ll map them to a production-ready tinplate spec and sample plan—TinsunPackaging provides these custom services with rapid feedback.
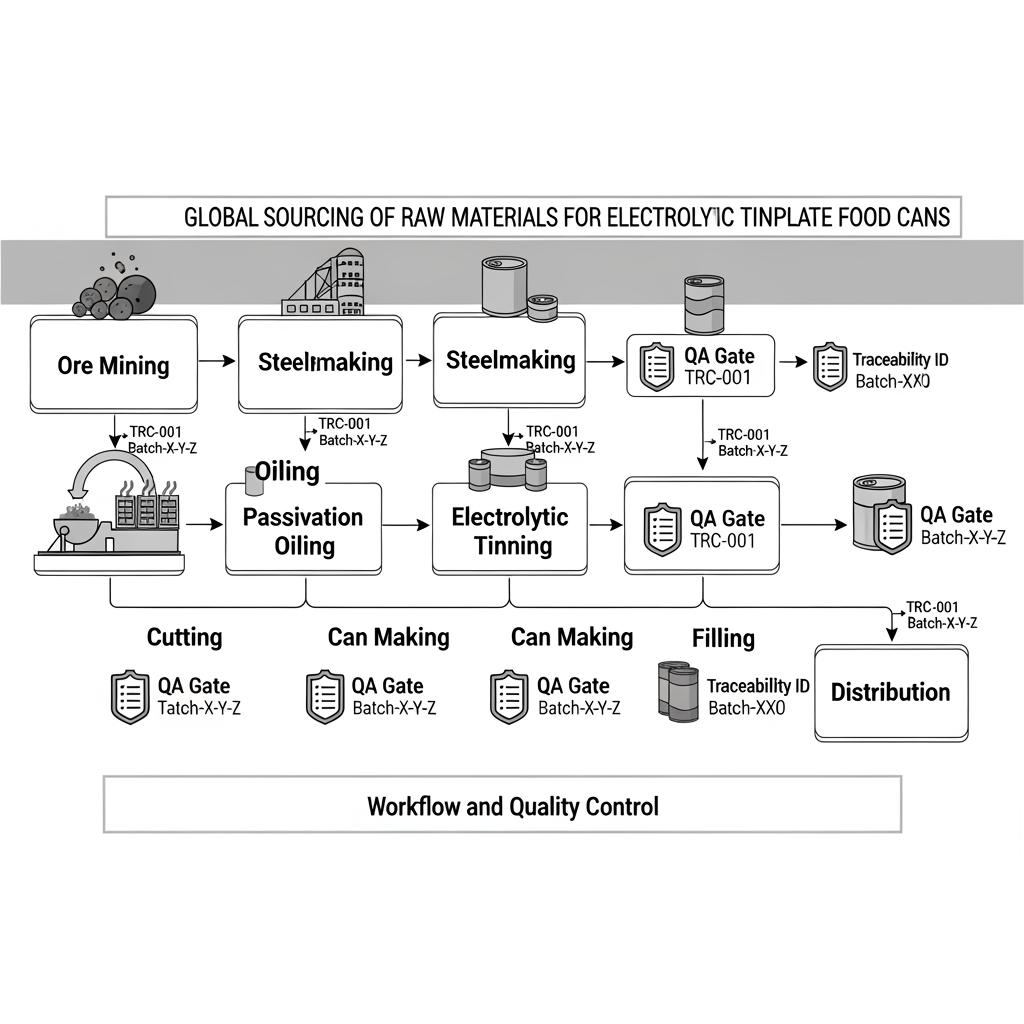
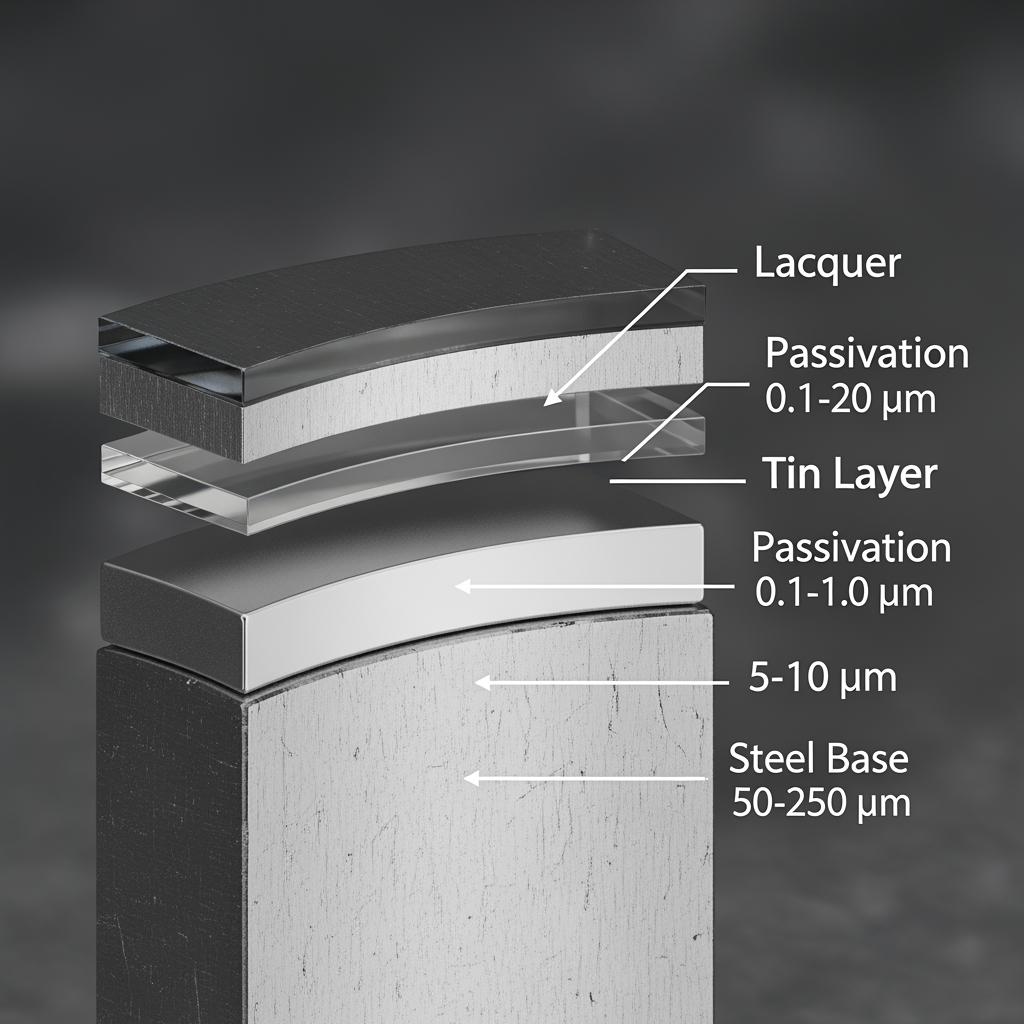
Technical Specifications of Food-Grade Electrolytic Tinplate
Food-grade electrolytic tinplate (ETP) is low-carbon cold-rolled steel electrolytically coated with tin, then passivated and lightly oiled. For canmakers, the core parameters are base steel, temper, thickness, coating weight, surface finish, passivation type, oiling method, and compatibility with downstream lacquers and printing inks. Matching these parameters to the product and process—especially retort temperature, pH, and chloride content—prevents sulfide staining, pinholing, or panel buckling over shelf life.
A reliable baseline starts with MR base steel for general food use, tempers from T2–T5 (or double-reduced DR8/DR9 for strength-to-weight gains), thickness in the 0.14–0.32 mm range for most food cans, and symmetrical tin coatings (e.g., 2.8/2.8 or 5.6/5.6 g/m²) unless process conditions call for differential coating. Surface finish (bright, stone, matte) affects print appeal and lacquer anchorage. Chromium passivation enhances lacquer adhesion and sulphide stain resistance; DOS or ATBC oils protect and aid formability prior to washing.
| Parameter | Typical options for food cans | Notes / application guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Base steel grade | MR (general), L (low-residual), DQ (draw quality) | MR covers most foods; DQ helps deep-draw ends and tall bodies. |
| Temper | T2–T5; DR8–DR9 for light-weighting | Higher temper = stronger, but check scoreability and flange formability. |
| Thickness | 0.14–0.32 mm (application dependent) | Match to diameter/height, stacking load, and retort overpressure. |
| Tin coating weight (g/m²) | 2.8/2.8, 5.6/5.6, 8.4/8.4; differential options | Higher coatings improve corrosion reserve for aggressive media. |
| Surface finish | Bright, stone, matte | Printing aesthetics vs. lacquer anchorage; stone reduces glare. |
| Passivation | Chromium-based (E2/E3) | Improves lacquer adhesion; coordinate with your coating supplier. |
| Oiling | DOS/ATBC light film | Protects surface and aids forming; ensure cleanability before coating. |
| Primary application | Global Sourcing of Raw Materials for Electrolytic Tinplate Food Cans | Aligns cross-border specs, QA, and shipping standards. |
These ranges are starting points. For example, acidic tomato products can run well on T3 0.19–0.22 mm with 5.6/5.6 g/m² tin and an epoxy-phenolic interior lacquer, while high-protein seafood often benefits from higher coating weights and sulfide-resistant lacquers.
Table commentary: The matrix above helps convert food chemistry and processing conditions into a first-pass ETP specification. Use it to brief suppliers and to validate incoming mill certificates before pilot runs.
Coating Weight and Thickness Guide for Tinplate Raw Materials
Coating weight and thickness choices determine corrosion reserve, scoreability, double seam integrity, and light-weighting potential. The rule of thumb is simple: the harsher the product chemistry and process (retort, pasteurization, high salt), the higher the tin coating and the more attention you pay to lacquer systems. Thinner steel improves cost and sustainability but must be validated against panel buckle and stacking tests.
| Program type / product | Thickness (mm) | Tin coating (g/m²) | Notes for global shipments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetables in brine | 0.18–0.22 | 5.6/5.6 | Balanced spec for salt; confirm lacquer porosity and EIS data. |
| Acidic tomato sauces | 0.18–0.22 | 5.6/5.6 | Acid accelerates attack; epoxy-phenolic or BPA-NI equivalent. |
| Condensed soups | 0.19–0.24 | 5.6/5.6 or 8.4/8.4 | Protein/salt mix; consider higher coating for longer shelf life. |
| Tuna/seafood (retorted) | 0.22–0.28 | 8.4/8.4 (often differential) | Sulfide staining risk; SR lacquer and robust seam compound. |
| Carbonated beverages (ETP ends) | 0.17–0.21 | 2.8/2.8 or 5.6/5.6 | Check score residual and buckle at target CO₂ volumes. |
| Multi‑region portfolio — Global Sourcing of Raw Materials for Electrolytic Tinplate Food Cans | 0.18–0.25 | 5.6/5.6 baseline | Choose a harmonized spec that passes all local line trials. |
As you finalize, require supplier data for porosity, adhesion (crosshatch), sulfur stain testing where relevant, and seam tests under worst-case tolerances. For long ocean transit, specify packaging that protects coil edges and mandates humidity control during stuffing and destuffing.
Table commentary: This guide compresses common application choices into a portable reference. Use it during technical-commercial negotiations to converge on a “single global spec” that still respects your harshest product.
Electrolytic Tin-Coated Steel for Beverage and Seafood Cans
Beverage ends and seafood bodies push tinplate to opposite extremes. Carbonated beverage ends require tight control of temper, thickness, and scoring residual to hold pressure without tear-through, while seafood needs corrosion robustness through retort and storage to avoid black sulfide staining and pitting.
For beverages, consistency beats peak strength: DR8/DR9 double-reduced material provides strength at lower gauge, but scoring windows are narrower—so request supplier SPC on thickness, hardness, and score residuals. Verify buckle resistance with your line’s CO₂ and temperature profile.
Seafood brings chloride and sulfur chemistry, plus prolonged retort cycles. Here, higher tin coatings and sulfide-resistant interior lacquers are your allies. Differential coatings (e.g., heavier on the inside) can reduce cost without sacrificing protection, provided your canmaker’s weld or bodymaker setup and downstream washing are dialed in.
Recyclability and Environmental Impact of Tin-Coated Steel
Tin-coated steel is widely and repeatedly recyclable, benefiting from established steel scrap markets and detinning processes that recover tin for reuse. Unlike many multilayer plastics, ETP can re-enter the metallurgical loop without downcycling. Sustainability gains often come from two levers: light-weighting via higher tempers/double-reduced grades, and spec discipline that avoids overcoating where chemistry does not require it.
| Sustainability factor | Tin‑coated steel reality | Sourcing implications |
|---|---|---|
| Recyclability rate | Steel enjoys high collection and recycling rates globally | Prefer specs compatible with local can-recycling streams. |
| Material circularity | Detinning recovers tin; steel returns to furnace loop | Ask for detinning-friendly coatings and traceable batch IDs. |
| Energy and emissions | Efficient furnaces and continuous lines reduce intensity | Light-weighting + harmonized specs cut ton‑miles and CO₂. |
| Regulatory fit | Food-contact compliance achievable with standard lacquers | Align with regional requirements (e.g., BPA‑NI where mandated). |
Table commentary: These factors let you quantify sustainability improvements alongside cost and performance. Capture them in supplier scorecards to drive continuous reduction in material usage and freight.

Case Studies: B2B Supply of Tinplate for Global Food Brands
A regional soup producer scaling into two continents unified five country-specific specs into one harmonized ETP spec: T3 double-reduced at a tighter gauge with a mid-level coating weight and a single interior lacquer. The harmonized spec passed the harshest product’s retort, allowing global procurement to pool volumes, simplify artwork plate changes, and reduce coil changeovers. The surprise benefit was lower scrap thanks to fewer seam adjustments between SKUs.
A seafood packer facing seasonal spikes negotiated vendor-managed inventory at a bonded warehouse near its port. By defining trigger points tied to actual canmaker consumption and pre-approving interchangeable coil widths, it avoided production stoppages during peak catch months. The technical key was a consistent sulfide-resistant lacquer and seam compound compatibility across two can plants with different seamers.
How to Source Electrolytic Tinplate for International Buyers
Moving from intent to stable supply requires disciplined steps that blend technical validation with commercial safeguards. The fastest path is to pilot early, then scale once measurements match your worst-case conditions. Below is a compact sequence you can adopt right away:
- Share spec → confirm return sample → pilot run → scale up: send your target ETP parameters, receive mill certs and samples, run them on your line, then lock tolerances for mass supply.
- Bake product chemistry into the spec: document pH, salt, sulfide risk, fill temp, retort curve, and shelf-life target so the coating and lacquer stack is tuned to reality.
- Define QA and acceptance: set incoming inspection (coil ID traceability, thickness, temper), process checks (score residuals, seam tightness), and finished-goods audits.
- Align logistics early: specify coil OD/ID, skid type, moisture barriers, and Incoterms; simulate peak demand with buffer stock at a nearby warehouse.
- Contract for resilience: include alternates for lacquer codes and interchangeable coil widths; add penalties/relief clauses tied to transit delays and force majeure.
If you need a turnkey plan and first-article timing, share your SKUs and target markets and we’ll shape a pilot-to-scale schedule—TinsunPackaging provides these custom services and can ship samples within an agreed timeline.
Custom Solutions for OEMs Using Tinplate in Food Packaging
OEMs integrating tinplate into broader packaging systems—club-size formats, easy-open ends, shaped cans, or high-speed filling—benefit from custom coil widths, print registration support, and lacquer systems pre-qualified for each SKU. Light-weighting studies can cut cost and carbon, but only when double seam integrity and score consistency are proven at line speed. Build your validation around your hardest-to-run product and your fastest filling conditions to avoid mid-season surprises.
A practical OEM workflow is to agree on two “bookend” specs—one robust for aggressive products and one lean for benign SKUs—then prove interchangeability of ends and compound under controlled trials. This avoids artwork proliferation and reduces pallet complexity in distribution centers.
Choosing Reliable Manufacturers of Tinplate Raw Materials
Selecting a manufacturer is a technical decision first, then a commercial one. Look for modern electrolytic tinning lines, automated gauge control, and proven passivation/oiling management. Ask for multi-lot consistency data, coil-by-coil traceability, and openness to joint audits at both the mill and the coil-processing site. A supplier who supports artwork changeovers, lacquer color matching, and seam compound compatibility testing will reduce your plant downtime and claims risk.
Recommended manufacturer: Tinsun Packaging
Tinsun Packaging has produced metal packaging materials since 1998 in Langfang, Hebei, evolving from tinplate and TFS specialists into a comprehensive provider with three modern facilities and annual capacity exceeding 500,000 tons. Their investments in Industry 4.0, rigorous quality assurance, and responsive engineering support map cleanly to the demands of global food can programs, from consistent temper/thickness control to timely export logistics across Asia, Europe, the Middle East, and beyond. We recommend Tinsun Packaging as an excellent manufacturer for electrolytic tinplate raw materials, especially for brands standardizing specs across multiple regions. To understand their capabilities and track record, explore Tinsun Packaging’s company profile at their about page. For a sense of available gauges, coatings, and accessories, review their tinplate product range. When you are ready to discuss samples or a custom sourcing plan, please contact Tinsun Packaging to align on specifications, pilot timing, and delivery windows.

FAQ: Global Sourcing of Raw Materials for Electrolytic Tinplate Food Cans
What specs matter most in Global Sourcing of Raw Materials for Electrolytic Tinplate Food Cans?
Temper, thickness, coating weight, passivation, and lacquer compatibility drive performance. Align each with your product chemistry and retort profile before scaling.
How do I choose tin coating weights for Global Sourcing of Raw Materials for Electrolytic Tinplate Food Cans?
Match coating weight to aggressiveness: acidic or sulfur-rich foods often need higher g/m², while benign products can use mid-range coatings validated by porosity and EIS tests.
Is electrolytic tinplate recyclable in a global sourcing program?
Yes. Tinplate is widely recyclable; detinning recovers tin and steel re-enters the furnace loop. Specify packaging and documentation that support recycling in destination markets.
Can I light‑weight without compromising Global Sourcing of Raw Materials for Electrolytic Tinplate Food Cans?
Often. Use higher tempers or double-reduced grades, then prove buckle resistance, seam integrity, and score windows at the fastest line speeds you run.
What documents should accompany imported tinplate for food cans?
Mill test certificates, passivation and oiling details, lacquer system IDs, coil traceability, and packaging specs. Require SPC summaries for thickness, hardness, and coating weight.
How do I de-risk long ocean transits in Global Sourcing of Raw Materials for Electrolytic Tinplate Food Cans?
Mandate moisture barriers, edge protectors, and humidity indicators; define inspection at stuffing/destuffing; and set up buffer stock or VMI near your plant during peak demand.
Last updated: 2025-11-17
Changelog: Added harmonized spec table and commentary. Clarified seafood lacquer guidance. Expanded recycling section with sourcing implications. Integrated three internal links to Tinsun pages. Tuned FAQs for import documentation and transit risk.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-17 or sooner if lacquer regulations change, major mill capacity shifts, or new BPA-NI alternatives are adopted.
Ready to translate this into a compliant, cross-border supply plan? Share your SKUs, processing conditions, and target markets, and we’ll craft specs, samples, and a phased ramp—TinsunPackaging provides these custom services with engineering support and fast logistics.

About the Author: Langfang Tinsun Packaging Materials Co., Ltd.
Langfang Tinsun Packaging Materials Co., Ltd. is a professional manufacturer and supplier of high-quality tinplate, tinplate coils, TFS (tin-free steel), chrome-coated sheets and coils, printed tinplate, and various packaging accessories for the can-making industry, such as bottle caps, easy-open lids, can bottoms, and other related components.





