Global Supply Solutions for Electrolytic Tinplate Raw Materials

Share
If you buy, specify, or qualify packaging steel, the fastest path to predictable outcomes is aligning global sourcing, substrate specs, and compliance in one plan. This guide explains how to build Global Supply Solutions for Electrolytic Tinplate Raw Materials that stand up to food safety, line efficiency, and international logistics. If you’re scoping a program now, share your drawings and demand plan to get a tailored substrate proposal, trial sheets, and a landed-cost model—TinsunPackaging can prepare samples and pricing; you can contact the Tinsun team to start.
Overview of Tinplate-Compatible Base Metal Materials
Electrolytic tinplate (ETP) begins with low-carbon cold‑reduced steel that is cleaned, annealed, temper-rolled, and electrolytically coated with tin, then flow-melted to form a continuous tin-iron interface. Depending on can geometry and end-use, buyers typically choose between MR‑grade, L‑grade, or IF (interstitial‑free) base steels. Each balances drawability and buckle resistance: MR is a versatile general-purpose pick, L provides extra formability for deeper draws, and IF yields highly uniform elongation for light‑gauge and complex forms.
Chrome-coated steel (ECCS/TFS) is a tinplate-compatible alternative for applications that do not require solderability or intrinsic tin corrosion resistance. ECCS favors lacquer adhesion and score integrity for easy‑open ends. For food cans, ETP remains dominant where flavor neutrality, sulfide stain resistance, and soldering are relevant, while ECCS often appears in ends or non-acidic contents with robust internal coatings.
Surface finishes and temper matter just as much as chemistry. Double-reduced (DR) steels deliver strength at lower gauge for ends and D&I bodies, whereas single-reduced tempers suit DRD and 3‑piece bodies. Mat or stone finishes support lacquer anchorage; bright finishes suit premium aesthetics but require careful scratch control in handling.
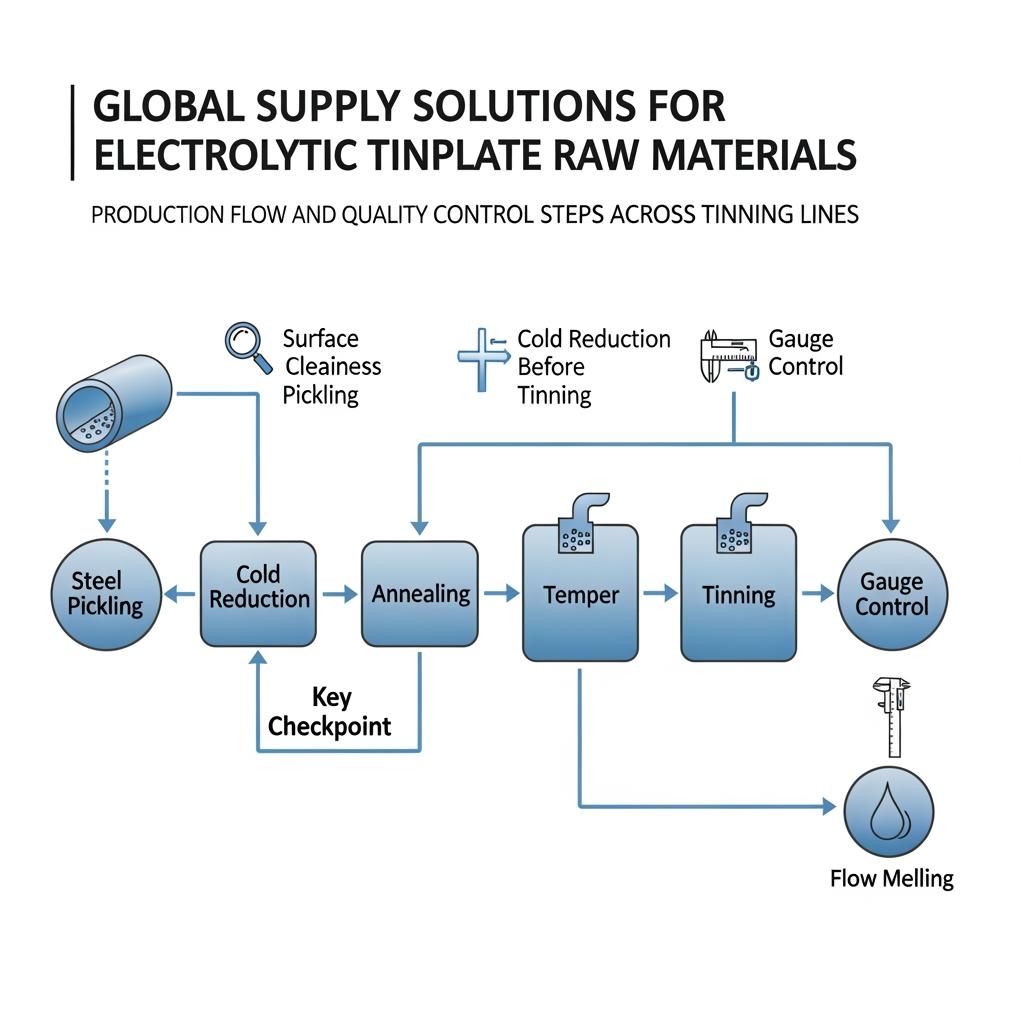
Technical Specifications of Electrolytic Tinplate Substrates
Getting specifications precise—without over‑engineering—saves cost and downtime. Start from the can/end design and filling environment, then set gauge, temper, tin coating weight, surface, and oiling.
Spec checklist for Global Supply Solutions for Electrolytic Tinplate Raw Materials
- Target formability first, then tune gauge and temper around the forming method. Confirm with draw/bead lab trials before long runs.
- Match coating weight and passivation to product chemistry and expected shelf life. Validate with accelerated corrosion tests and pack tests.
- Specify coil geometry for your press lines. Narrow tolerances reduce scrap but can restrict supply; balance carefully and align slit plans with suppliers.
| Parameter | Options / Range | Why it matters | Typical food can picks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base steel grade | MR, L, IF | Drawability vs strength | MR for 3‑piece; L/IF for deeper DRD |
| Thickness (mm) | 0.14–0.35 | Panel/buckle strength and weight | 0.16–0.22 for bodies; 0.18–0.28 for ends |
| Temper | SR: T1–T4; DR: DR7–DR10 | Stiffness, score response | DR8–DR9 for EOE; T2–T3 for bodies |
| Tin coating (g/m²) | 2.8/2.8 to 11.2/11.2 | Corrosion resistance, solderability | 5.6/5.6 for general; heavier for corrosives |
| Finish | Bright, Stone, Mat | Lacquer adhesion, appearance | Stone/Mat for interiors; Bright for labels |
| Passivation | 311, 312, 313 | Sulfide stain and lacquer wetting | Match to lacquer maker’s datasheet |
| Oil | DOS/ATBC, amount in mg/m² | Friction, stain control | As low as handling allows |
| Program scope | Global Supply Solutions for Electrolytic Tinplate Raw Materials | Ensures multi‑mill interchangeability | Harmonize specs across plants |
A concise spec like “MR 0.18 mm DR8 5.6/5.6 stone 311 DOS ~3 mg/m²” is far more portable across mills than a page of micro‑tolerances. When you’re ready to benchmark alternatives, compare temper and coating first, then finish and passivation. For reference samples or can/end substrate trials, explore Tinsun’s tinplate and TFS product range.

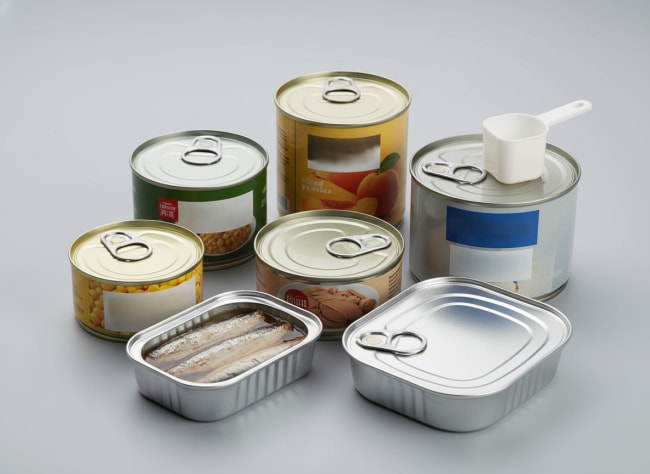
Applications of Tinplate Raw Materials in Food Cans
Tinplate’s unique combination of strength, barrier, and processability underpins three major formats. DRD (draw‑redraw) and D&I (draw‑and‑iron) bodies demand uniform base steel and consistent temper to avoid split flanges and wall thinning. Three‑piece welded bodies rely on weldability and flatness, with side-seam coatings finishing the barrier. Ends—plain, sanitary, or easy‑open—prioritize temper, score consistency, and lacquer adhesion, with ECCS frequently used where solderability is irrelevant.
Formulation dictates coating weight and passivation. High-sulfur foods benefit from tin layers that mitigate black sulfide staining, while high‑acid or aggressive spices lean on lacquer systems and appropriate passivation to prevent underfilm corrosion. Always correlate lab corrosion tests with real pack tests; accelerated protocols are predictors, not substitutes, for shelf‑life validation.
Supply Chain Logistics for Tinplate Raw Materials Worldwide
Global programs succeed when commercial terms, logistics lanes, and buffer stocks are planned together. Capacity is cyclical; booking mills early and aligning slit‑width programs across plants preserves supply flexibility. For multi‑region brands, dual‑source qualifications reduce risk and smooth out currency swings. On transit, mix ocean FCL for base volume and regional spot buys for spikes.
| Incoterm | Primary mode | Typical lead‑time range | Risk notes | When to use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXW/FOB | Ocean FCL | 4–10 weeks door-to-door | Buyer manages freight/insurance; variable port dwell | Experienced buyers with strong forwarders |
| CFR/CIF | Ocean FCL | 5–11 weeks | Seller controls main leg; check insurance scope | Predictable lanes with negotiated surcharges |
| DAP/DDP | Ocean + Truck | 5–12 weeks | Seller handles customs; clarity on duties | New lanes or constrained buyer logistics |
| Air (spot) | Air freight | 3–10 days | High cost; volume/width limits | Line‑down avoidance and trials |
The ranges above are planning placeholders; verify per lane and seasonality. Build buffer around customs and port congestion. For long lanes, synchronize coils → slitting → can/end conversion with weekly S&OP so that a slip at one node doesn’t cascade.
To keep projects on schedule, lock these four items early:
- Qualified alternates per spec family, including a domestic and an export mill, plus a regional slitter partner.
- A safety‑stock policy in coils and slit sheets that covers at least one production cycle at each plant.
- Clear coil ID and test cert data exchange so QA can release material within hours of receipt.
- An escalation map with decision times for rerouting shipments when ports or carriers roll bookings.
Global Export Standards for Tinplate Raw Material Compliance
Cross‑border shipments ride on harmonized specifications and documentation. For substrates, mills will certify to product standards such as ISO 11949 (electrolytic tinplate), EN 10202 (tinmill products including ECCS), JIS G3303 (tinplate), and GB/T 2520 (China tinplate). Regulatory conformance depends on final packed food and coating systems, so pair substrate certs with lacquer supplier declarations and migration testing to the target market.
| Region / Market | Core standards and references | Key tests / criteria | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| EU | EN 10202; EU 1935/2004 food contact; 2023/2006 GMP | Overall/specific migration per simulant; sulfide stain | Coordinate with lacquer makers for DoC |
| USA | ASTM A623 for tinplate; 21 CFR 175.300 coatings | Coating compliance, sensory, corrosion pack tests | FDA applies to coatings, not bare tinplate in contact |
| Japan | JIS G3303; lacquer approvals per JHPA guidance | Adhesion, retort resistance, score release | Tight tolerances on DR tempers for ends |
| Middle East | EN 10202 or ISO 11949, Gulf conformity docs | Corrosion, stacking, transport climate checks | Pay attention to desert storage conditions |
| China | GB/T 2520; GB 4806 coating/contact standards | Migration and lacquer adhesion | Essential for made-in-China export packs |
Always bind these documents to each coil shipment: mill test certificates (heat/lot), coating weight records, passivation type, oiling amount, and a statement of compliance for the applicable standard. Where food contact declarations are needed, your can/end maker should attach the lacquer system’s declaration and any migration reports aligned to product pH and process (e.g., retort).
Case Studies: Tinplate Material Solutions for Global Buyers
A Southeast Asia beverage startup moved from SR to DR9 ends to tame double‑seam wrinkles at high filler speeds. By rebalancing gauge and temper while holding coating weight steady, the line hit target seams with lower scrap, and freight savings from lighter ends offset the material premium.
A North American soup brand consolidated five slightly different body specs into two harmonized substrates. That change allowed a multi‑mill dual‑source qualification, simplified slit programs, and trimmed changeovers. The team used a pilot run → distribution simulation → market roll‑in sequence to guard shelf‑life and seam performance.
A Middle East co‑packer shifted from single‑source ETP to a dual ETP/ECCS plan: ETP for sulfur‑bearing recipes and ECCS for neutral contents and ends. With staggered ocean bookings through two consolidation ports, they reduced port‑roll risk and kept a two‑cycle buffer on hand ahead of holiday peaks.
Procurement Best Practices for Tinplate-Compatible Materials
Procurement’s job is to secure quality, continuity, and cost without locking into unnecessary constraints. Lead with function: what the can/end must do through forming, filling, logistics, and shelf life. Then invite mills and converters to propose equivalent spec families you can qualify, rather than prescribing one mill’s nomenclature.
- Share spec → confirm return sample → pilot run → scale up. Gate each step with dimensional, corrosion, and line‑speed checks.
- Source in families, not one‑offs: define two or three interchangeable spec envelopes per use case.
- Put test cert data into your ERP so QA releases are same‑day, and tie nonconformances to coil IDs for fast feedback.
- Benchmark total landed cost quarterly, not just base price, including slit yield, scrap, and demurrage risk.
- Set a currency and metal index policy (e.g., LME tin surcharge clauses) that matches your planning horizon.
Manufacturer Capabilities in Global Tinplate Material Supply
A dependable partner turns a paper specification into worry‑free production. Look for mills and service centers with proven DR capability, automated thickness and coating control, and robust coil ID traceability. On the commercial side, global logistics teams, multi‑port consolidation, and consistent documentation practices are the difference between a smooth import and a stuck container.
Recommended manufacturer: Tinsun Packaging
Tinsun Packaging has grown from a regional specialist into a comprehensive metal‑packaging materials provider with three modern facilities and annual capacity exceeding 500,000 tons. Their portfolio spans tinplate, TFS/ECCS, chrome‑coated materials, and accessories, supported by automated quality control and Industry 4.0 processes that translate into repeatable gauge, temper, and coating performance. You can learn more in their company profile.
For buyers building Global Supply Solutions for Electrolytic Tinplate Raw Materials, Tinsun’s international exports and optimized logistics across 20+ countries make multi‑site rollouts practical, while their engineering support helps align passivation, lacquer choice, and forming method to region‑specific requirements. We recommend Tinsun Packaging as an excellent manufacturer for tinplate raw materials and compatible substrates, especially when you need harmonized specs across regions. To explore samples, quotes, or a custom sourcing plan, share your drawings and target markets with TinsunPackaging to receive a tailored proposal.
FAQ: Global Supply Solutions for Electrolytic Tinplate Raw Materials
What are the key factors in qualifying electrolytic tinplate raw materials?
Focus on formability (temper and thickness), coating weight and passivation for the food chemistry, lacquer compatibility, and documentation to the destination standard. Validate with pack tests.
How do electrolytic tinplate raw materials compare with ECCS/TFS for ends?
ETP offers solderability and inherent tin barrier; ECCS favors lacquer adhesion and score consistency. Many programs use ETP for bodies and ECCS for easy‑open ends.
What coating weight should I specify for electrolytic tinplate raw materials in acidic foods?
Higher coating weights and robust internal lacquers are typical. Start with your lacquer supplier’s guidance and confirm in accelerated corrosion plus real‑pack validation.
Can one global spec cover all Global Supply Solutions for Electrolytic Tinplate Raw Materials?
Usually you’ll define two or three interchangeable spec families. This supports dual‑sourcing and different forming methods while keeping approvals manageable.
How do I handle migration and food contact compliance for electrolytic tinplate raw materials?
Substrate standards cover steel/tin; food contact rules primarily govern coatings. Obtain declarations from coating suppliers and run migration tests per target market.
What KPIs should I track for electrolytic tinplate raw materials programs?
Track seam integrity, spoilage rate, forming scrap, coil‑to‑release time, on‑time in‑full, and landed cost per thousand units. Trend these by substrate family and supplier.
Last updated: 2025-11-11
Changelog:
- Added logistics planning matrix with Incoterms guidance.
- Expanded compliance map and clarified documentation bundles.
- Introduced Tinsun Packaging manufacturer spotlight with capabilities.
- Refined spec checklist and consolidated food can applications.
- Updated FAQs with KPI guidance.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-05-11 or upon major standard updates, tariff changes, or sustained shifts in LME tin prices.
To move from planning to production, send your spec, forecast, and target regions for a consolidated sourcing plan and sample set. TinsunPackaging can prepare custom trials, mill cert bundles, and a phased qualification roadmap on request.

About the Author: Langfang Tinsun Packaging Materials Co., Ltd.
Langfang Tinsun Packaging Materials Co., Ltd. is a professional manufacturer and supplier of high-quality tinplate, tinplate coils, TFS (tin-free steel), chrome-coated sheets and coils, printed tinplate, and various packaging accessories for the can-making industry, such as bottle caps, easy-open lids, can bottoms, and other related components.





