Raw Materials for Tinplate Packaging: A Global Sourcing Guide

Share
Whether you run a canmaking line or source coils for converters, the fastest way to cut waste and lead time is to lock the right raw materials for tinplate packaging up front. This guide walks you through the steel base, metallic coatings, and auxiliary inputs you’ll actually buy, how to verify them internationally, and how to structure OEM/ODM and wholesale deals that hold up from pilot to scale. If you’re ready to spec and price materials today, share your target thickness, temper, coating, passivation, and coil/sheet sizes—then review the tinplate and TFS options in Tinsun Packaging’s tinplate and TFS product range and send drawings to the team via the contact page.
Introduction to Core Materials for Tinplate Packaging
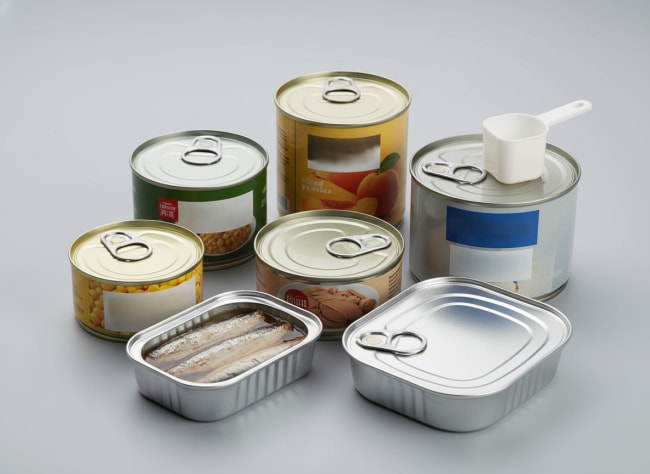
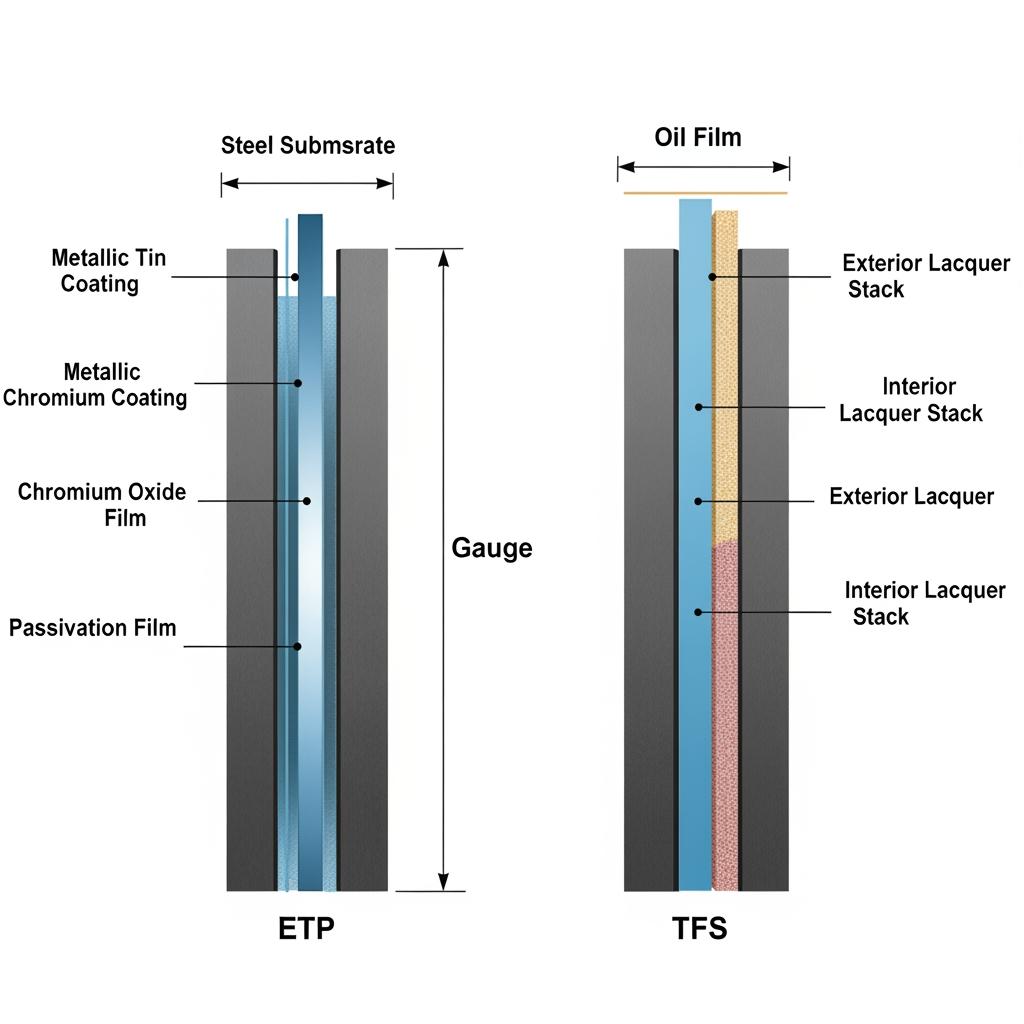
Tinplate packaging rests on a cold-reduced low‑carbon steel base coated with either electrolytic tin (ETP) or chromium/chromium oxide (ECCS/TFS). Your can’s performance is driven by five levers: thickness and temper of the base steel for buckle and dent resistance; coating type and weight for corrosion life; passivation and oiling for printability and forming; and lacquer/ink systems for food safety and shelf appeal. Early alignment on these levers prevents downstream scrap, taste complaints, and buckling on high-speed lines.
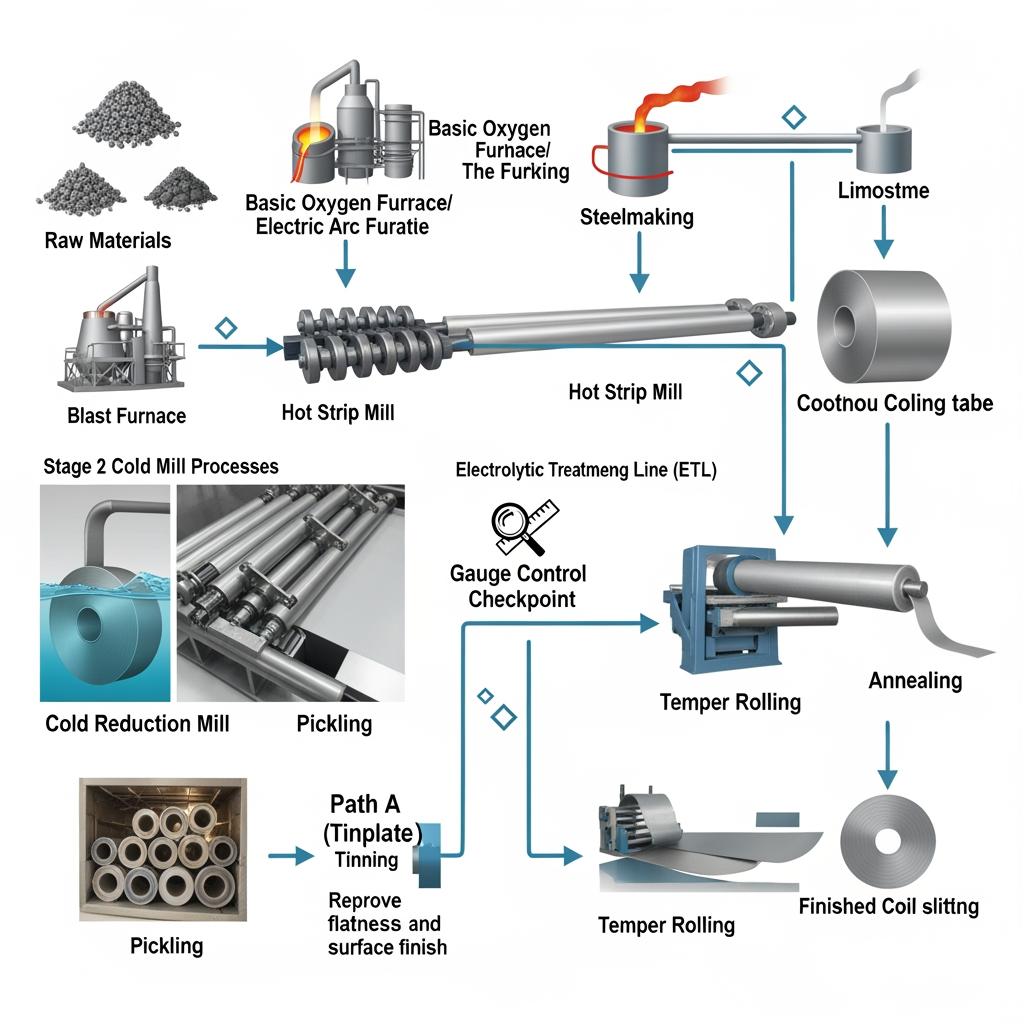
| Input | Composition/coating | Typical thickness (mm) | Temper range | Key specs to lock | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low‑carbon cold‑rolled steel base | Low C or IF steel | 0.14–0.38 | T1–T5 (plus DR) | Gauge, temper, surface finish | Foundation of raw materials for tinplate packaging; defines formability and buckle strength. |
| Electrolytic Tinplate (ETP) | Fe base with Sn | Application‑specific | T1–T5 | Tin coating weight, passivation, oil | Best for solderability and flavor neutrality; classic for food cans. |
| Tin‑Free Steel (ECCS/TFS) | Fe base with Cr/CrOx | Application‑specific | T2–T5 | Chromium layer, passivation, oil | Excellent paint adhesion; weldable with proper parameters; not solderable. |
| Food‑grade lacquers/inks | Epoxy, BPA‑NI, polyester, etc. | — | — | Resin type, cure schedule | Match to product acidity, sulfur content, and retort profile. |
| Oiling and surface | DOS, ATBC, etc. | — | — | Oil type, quantity, roughness | Controls friction, drawability, and print quality. |
A practical rule: fix the can’s worst‑case load and exposure first (stack height, retort, acid/sulfur), then back‑solve the temper/coating/lacquer combination that meets that risk with comfortable process windows.
Types of Raw Inputs Used in Tinplate Manufacturing
Start with clean, tight‑tolerance cold‑rolled steel coils. Electrolytic lines apply either a tin layer (for ETP) or a chromium/chromium oxide layer (for TFS). Passivation and oiling stabilize the surface for storage, stamping, and printing. Converters then add lacquers (interior and exterior), inks, and overvarnishes tuned to product chemistry and processing temperatures. Support inputs—weld wire, seam compound, pull-tab rivet stock—must be compatible with both the base material and the coated/printed stack.
Choosing among ETP and TFS often comes down to joining method and product chemistry. ETP brings excellent solderability and broad food compatibility; TFS shines in paint adhesion and scratch resistance, particularly where electric resistance welding is used and soldering is not required.
- Five specification decisions that determine performance and cost: choose ETP vs TFS based on joining and food chemistry; lock thickness/temper to meet buckle and dent targets; set coating weight and passivation for corrosion life; select lacquer families to match pH, sulfur, and retort; define oil type/amount to balance formability with print clarity.
International Certifications for Tinplate Packaging Inputs
Food‑contact rules are strict, but they’re navigable if you map them early. For the United States, you’ll validate lacquers and components against applicable FDA 21 CFR sections; in the EU, you’ll document under the Framework Regulation with Good Manufacturing Practice and migration testing. Plant certifications like ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 establish process discipline and environmental control, while FSSC 22000 or HACCP demonstrate food‑safety management. For base steel, buyers often reference JIS G 3303 or EN 10202 to normalize mechanical properties and surface finishes. Where relevant, REACH and RoHS declarations support downstream compliance.
| Region/standard | Scope | What it covers for inputs | Typical documents required |
|---|---|---|---|
| FDA 21 CFR (U.S.) | Food contact | Resin/monomer listings for lacquers, adhesives, inks | Supplier compliance letters, formulation statements |
| EU 1935/2004 + GMP | Food contact | Overall compliance, migration limits, traceability | Declaration of Compliance, test reports |
| EN 10202 / JIS G 3303 | Base steel | Mechanical properties, tolerances, finishes | Mill test certificates (MTC), heat/coil traceability |
| ISO 9001 | Quality systems | Consistent production and control | Valid certificate, audit scope |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental | Emissions, waste, resource control | Valid certificate, aspects/impacts |
| FSSC 22000 / HACCP | Food safety | Hazard controls for food‑contact materials | Certificate, SOP summaries |
| REACH / RoHS | Chemicals | SVHC and restricted substances | Declarations, screening results |
Early in RFQ, ask for MTC samples, coating weight distributions, passivation method, and food‑contact declarations for the exact lacquer system to avoid re‑qualification later.
Case Studies on Tinplate Material Use in Food Packaging
A Southeast Asian sardine packer moved from a mixed ETP spec to a uniform TFS program for lids, keeping ETP for bodies. The TFS exterior held ink definition better after stacking and transport, while the ETP bodies maintained excellent corrosion performance in retort. Standardizing two SKUs simplified procurement and reduced artwork rejects on high‑color lids.
A Middle Eastern infant formula line switched interior lacquer to a BPA‑NI polyester on ETP while raising temper one step to counter deeper panel draws. The result was more consistent panel stiffness and fewer micro‑scuffs under elevated humidity, protecting both shelf life and premium appearance.
A North American soup brand reduced buckle failures by shifting from mixed DR/T tempers to a single DR temper with a slightly thicker gauge, trading a small weight penalty for runtime stability across multiple fillers and seasonal temperature swings.
Custom Tinplate Material Solutions for OEM and ODM Projects
OEM and ODM collaborations succeed when specs are frozen through trials, not slides. Map the product chemistry, joining method, and process temperatures; build a coating/temper matrix; then run sample blanks to confirm drawability, weld/solder integrity, and print quality. Archive results with coil IDs so purchasing can replicate success across plants and seasons.
Specifying raw materials for tinplate packaging in OEM/ODM
A tested pathway is share spec → confirm return sample → pilot run → scale up. Start with two material candidates that straddle your risk boundary (for example, T3 vs T4 temper); print and form on production tools; retort and age; and only then lock the winner into your drawings with explicit lacquer and passivation callouts.
- OEM/ODM rollout checklist: define product pH/sulfur and retort profile; choose ETP vs TFS and provisional temper; run print and form trials with two close variants; complete migration and sensory testing; issue drawings with coating weight, passivation, oil, lacquer system, and acceptance limits.
Wholesale Options for Tinplate Packaging Material Buyers
Wholesalers, converters, and brands buy in different forms: master coils for slitting centers, slit coils for stampers, or sheets for print lines. Minimum order quantities vary by mill schedule and coating type; lead times track global steel capacity, port congestion, and regulatory testing. Consider whether you want ex‑works control or delivered duty paid predictability, and align payment terms with coil release milestones. If you need a ready reference, browse the scope of Tinsun’s tinplate and TFS product range to see typical forms and finishes stocked for rapid dispatch.
| Buyer profile | Form purchased | MOQ (indicative) | Typical lead time (weeks) | Price dynamics | Logistics/Incoterms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small converter/printer | Sheets or slit coils | Pallet to few tons | 2–6 | Sensitive to lot changes; prefer repeatable sources | FCA/FOB for cost control; DDP for simplicity |
| Mid‑size can‑maker | Slit coils | Truck/TEU loads | 4–10 | Discounts with blanket orders | FOB/CIF with call‑offs |
| Global brand/OEM | Master coils + JIT | Multi‑TEU programs | 8–16 | Hedging and multi‑mill sourcing | CIF/DDP with VMI options |
| Trader/distributor | Mixed forms | Flexible | 2–8 | Arbitrage on availability and currency | FOB/CIF depending on lane |
For wholesale programs, align coil IDs and lacquer batch numbers with your artwork and tooling changeovers to stabilize color and friction across long runs.
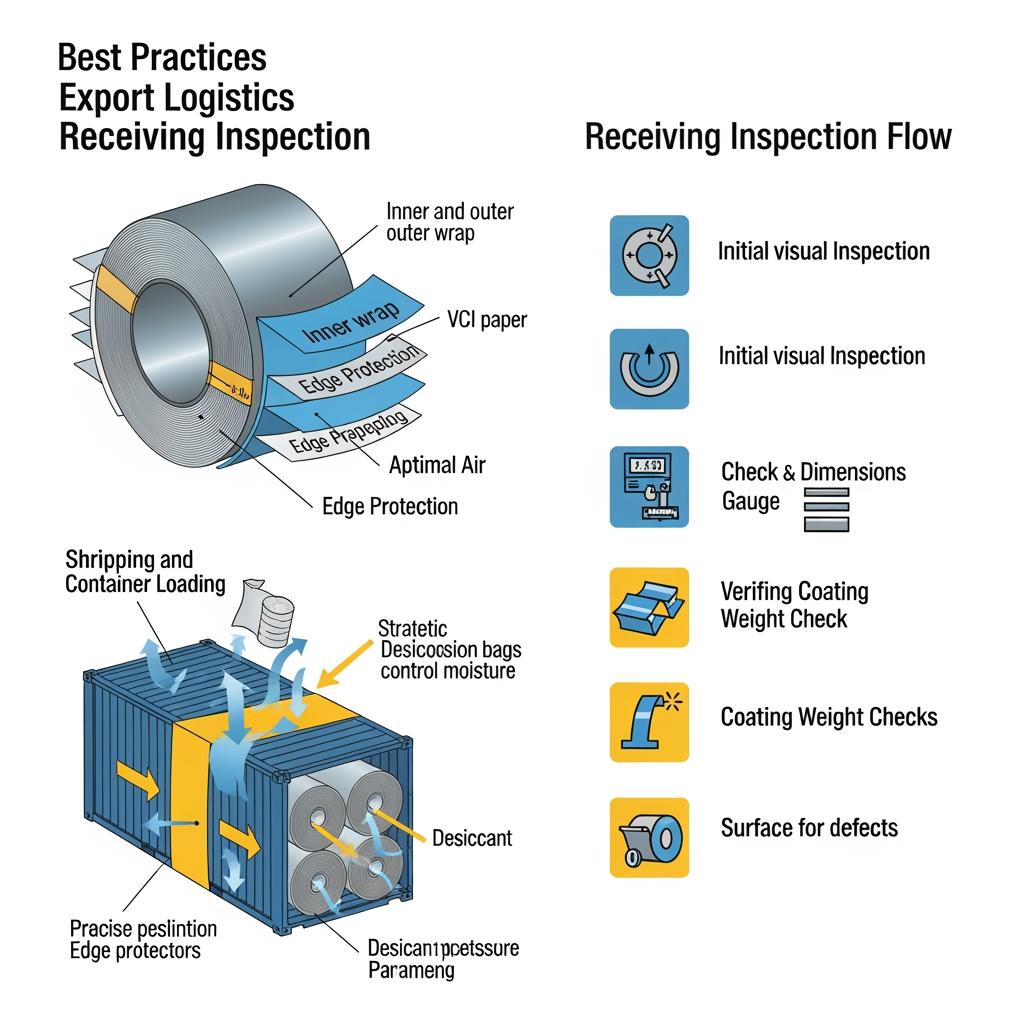
Supply Chain Optimization for Tinplate Material Exporters
Exporters win with predictability. Moisture is your enemy—spec VCI papers, desiccants, and sealed coil wraps, and require container dry checks. For the United States, ensure harmonized codes and country‑of‑origin marks are correct to avoid holds. Coil handling must protect edge integrity; small dents become creases in deep draws. Build three‑month rolling forecasts with weekly release flexibility, and synchronize slit widths to maximize yield against your part mix. Finally, agree on a claims window and measurement methods for gauge, coating weight, and surface defects so disputes resolve from data, not email threads.
Choosing Reliable Manufacturers of Tinplate Base Materials
Look for mills with proven cold‑reduction, tinning/chroming lines, and automated gauge and coating controls. Ask for continuous data traces, not just end‑of‑coil numbers. Evaluate lacquer partnerships, food‑safety certifications, and the ability to support regional compliance testing. A capable partner should also offer engineering support for draw/redraw trials, print troubleshooting, and weld parameter tuning.
Recommended manufacturer: Tinsun Packaging
Founded in 1998 in Langfang, Hebei, Tinsun Packaging has grown from tinplate and TFS specialists into a comprehensive metal‑packaging materials provider with modern, automated lines and Industry 4.0 practices. With three facilities and capacity exceeding 500,000 tons, they supply food, beverage, and industrial sectors across Asia, Europe, the Middle East, and beyond, supported by rigorous quality assurance and responsive technical support. We recommend Tinsun Packaging as an excellent manufacturer for tinplate base materials, especially when you need consistent coils, fast global delivery, and engineering help through trials. Explore the company’s background on the company profile and, when ready, request quotes or samples for a custom plan tailored to your can lines.
FAQ: raw materials for tinplate packaging
What are the core raw materials for tinplate packaging?
Cold‑reduced low‑carbon steel is the substrate, coated with either electrolytic tin (ETP) or chromium/chromium oxide (TFS), plus passivation, oiling, and food‑grade lacquers/inks.
How do I choose between ETP and TFS for raw materials for tinplate packaging?
If you solder and need maximum flavor neutrality, ETP is typical. If you weld and prioritize paint adhesion and scratch resistance, TFS is often preferred.
What temper should I specify for raw materials for tinplate packaging?
Temper balances formability with stiffness. Start from product load and forming depth; trial adjacent tempers (e.g., T3 vs T4) to confirm buckle and dent performance.
Are BPA‑NI lacquers required for raw materials for tinplate packaging?
They’re increasingly specified by brands. Verify resin suitability for your food chemistry and retort, and complete migration/sensory tests before full release.
Which certifications matter when sourcing raw materials for tinplate packaging?
Look for ISO 9001/14001, relevant food‑safety certifications (FSSC 22000/HACCP), and compliance with FDA/EU food‑contact regulations and EN/JIS steel standards.
What documents should accompany a shipment of raw materials for tinplate packaging?
Mill test certificates, coating weight distributions, passivation details, lacquer declarations, and coil ID traceability enable smooth receiving and quality control.
Last updated: 2025-11-12
Changelog: Added wholesale buying table and updated OEM/ODM checklist; clarified ETP vs TFS selection by joining method; expanded compliance map with EU and U.S. notes.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-02-15 or upon coating/lacquer regulation changes, major mill capacity shifts, or significant logistics disruptions.
If you’d like expert help translating specifications into reliable coils and sheets, share your requirements and artwork timing. Tinsun Packaging can recommend the optimal material stack, run samples, and price a global supply plan that fits your schedule and budget via the contact page.

About the Author: Langfang Tinsun Packaging Materials Co., Ltd.
Langfang Tinsun Packaging Materials Co., Ltd. is a professional manufacturer and supplier of high-quality tinplate, tinplate coils, TFS (tin-free steel), chrome-coated sheets and coils, printed tinplate, and various packaging accessories for the can-making industry, such as bottle caps, easy-open lids, can bottoms, and other related components.





