High-Performance Tinplate for Alkaline Battery Sleeve Protection

Share
High-Performance Tinplate for Alkaline Battery Sleeve Protection is a niche specification of electrolytic tin-coated steel engineered to resist alkaline chemistry, forming stresses, and long shelf-life demands. The fastest way to de-risk your next battery sleeve program is to align coating mass, base steel temper, and passivation with your electrolyte and form factor from day one. If you already have drawings, share them and request a small pilot coil—Tinsun Packaging can cut, oil, and temper-match a custom tinplate to your exact sleeve geometry. To see options you can start with today, browse the battery tinplate product range and request samples through our battery tinplate product range page.
Tin-Coating Specifications for Battery-Grade Steel Materials
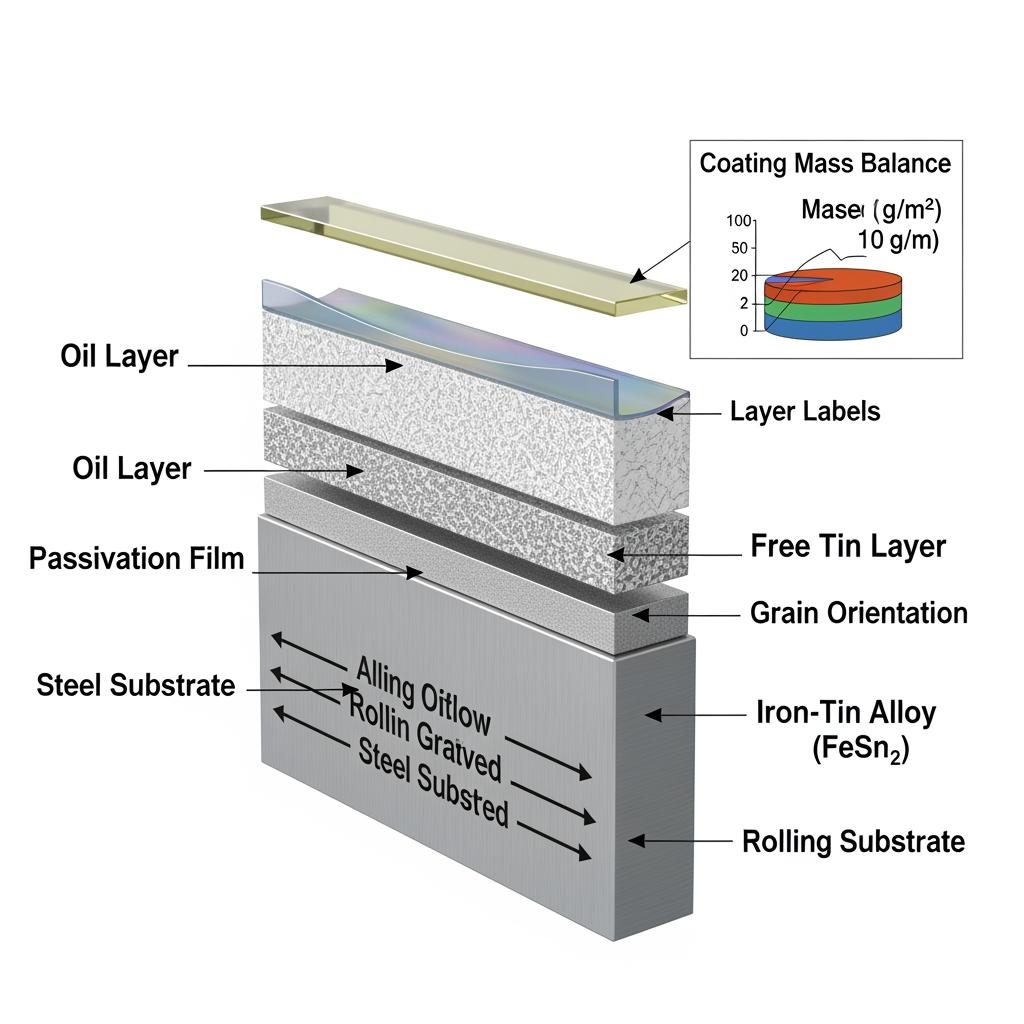
For sleeves that must survive deep draw, roll seam, and crimping without flaking or edge corrosion, three levers control performance: base steel grade and temper, tin coating mass and balance (differential or equal), and post-treatment (passivation and oil). In alkaline cells, a light-to-medium tin coating with consistent alloy layer growth typically offers the best blend of solderability, printability, and sacrificial protection. Most AA/AAA sleeves prefer moderate tempers for formability, while larger C/D sleeves can move up a step for hoop strength. When in doubt, run a forming coupon and an immersion test in your own electrolyte to confirm the window.
| Parameter | Typical options for battery sleeves | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Base steel & temper | Low-carbon, single reduced; work with tempers in the mid range for AA/AAA, higher for C/D | Balances hoop strength with elongation so sleeves form without split or springback. |
| Tin coating mass (both sides) | Light to medium (e.g., ~2.8/2.8 to ~5.6/5.6 g/m²) depending on size and electrolyte | More tin improves sacrificial behavior, but too much can raise cost and affect lacquer wetting. |
| Coating balance | Equal or slightly differential (inside-biased) | Inside-biased tin helps where electrolyte contact is more aggressive. |
| Surface finish | Bright or stone | Influences print quality, lacquer adhesion, and seam conductivity during welding. |
| Passivation | Modern trivalent systems tuned for RoHS/REACH | Stabilizes free tin against oxidation and improves scratch resistance. |
| Oil/lube | DOS or compatible forming oil, application controlled at mill | Reduces galling in draw/ironing and helps coil handling. |
| Application note | Spec tuned for High-Performance Tinplate for Alkaline Battery Sleeve Protection in AA/AAA sleeves | Keeps forming yield high while preserving corrosion resistance in service. |
Select values should always be confirmed by pilot forming and electrolyte exposure. The table gives a decision frame; the exact numbers should be validated by your internal tests and supplier certificates.
Corrosion Resistance of Tinplate in Battery Sleeve Applications
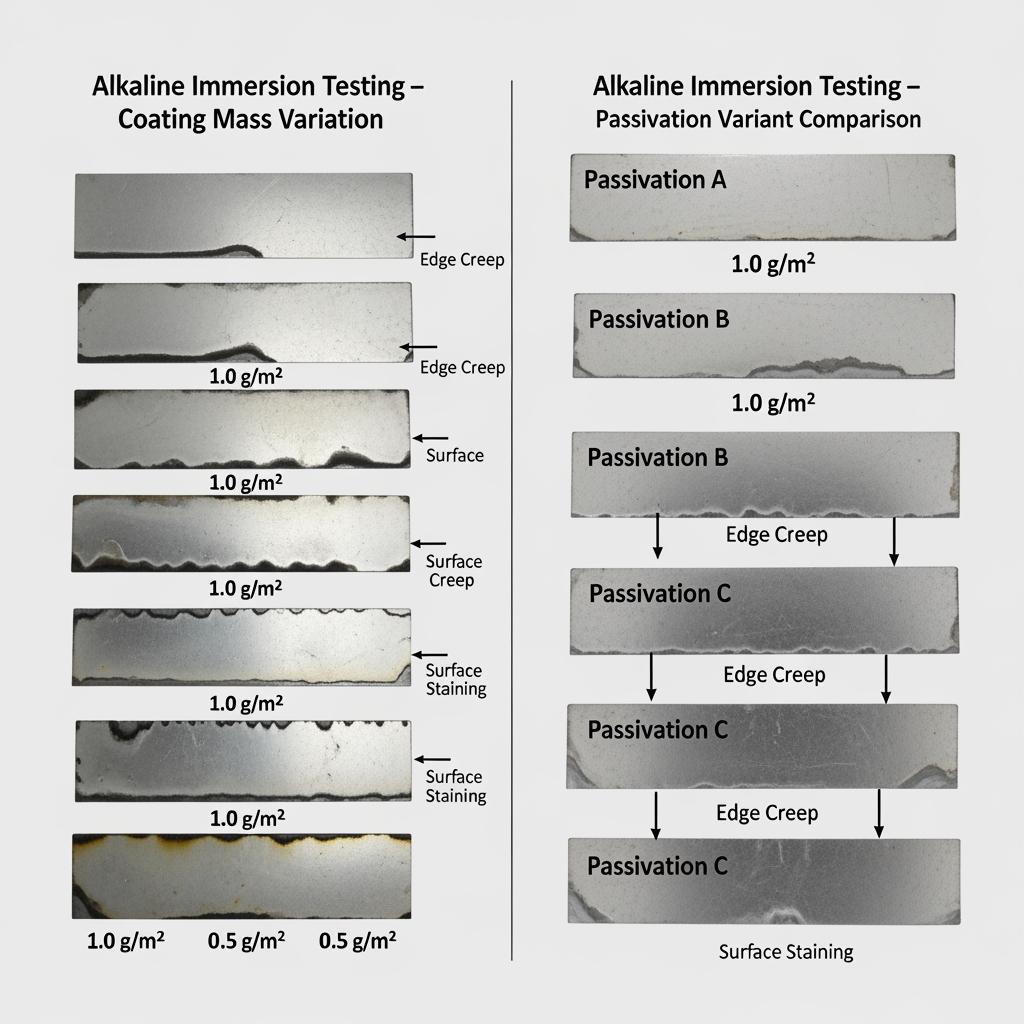
Alkaline batteries operate near pH 13–14 with KOH or NaOH electrolytes. In this environment, tin provides sacrificial protection while the alloy layer limits underfilm creep. The goal is to slow initial attack, prevent edge rust, and avoid discoloration under printed labels or lacquers. Three practical checks help: immersion in your electrolyte (room and elevated temperatures), edge creep measurement on sheared samples, and lacquer adhesion after humidity cycling. If you see blackening or underfilm creep, adjust passivation and inside coating mass before moving to heavier lacquers.
| Electrolyte or exposure | Expected risk level | Mitigation on tinplate | In-application note |
|---|---|---|---|
| KOH electrolyte splash/condensate | Medium to high near edges | Increase inside tin balance, upgrade passivation, consider edge lacquer | Focus on cut-edge sealing and uniform oil removal before coating. |
| NaOH electrolyte | Medium | Similar mitigations; verify lacquer chemistry compatibility | NaOH may stain differently; check visual criteria with QA. |
| Salt/humidity storage (non-electrolyte) | Low to medium if packaging traps moisture | Use vapor-phase inhibitors in packaging; maintain coil wrap integrity | Storage controls can prevent transport rust that looks like in-service attack. |
| Mixed-metal contact (fixtures/spacers) | Variable | Avoid galvanically dissimilar contacts; use isolators | Prevents localized corrosion marks after forming delays. |
Run these tests with your actual lacquer and adhesive stack; the surface energy of the tinplate after passivation and oil removal meaningfully changes lacquer wetting and, eventually, corrosion performance.
Explosion Resistance of Electrolytic Tinplate in Battery Use
Strictly speaking, sleeves do not “explode”; instead, pressure rise from gassing can challenge hoop strength and seam integrity. Your safety envelope depends on temper (yield strength), thickness, sleeve diameter, and weld or lock-seam design. In practice, you want enough strength margin so sleeves tolerate transient pressure without permanent growth that misaligns the label or compromises terminal fit.
A robust validation plan couples forming tests with controlled pressurization and seam peel. Integrate ring crush or burst-style fixtures with your battery’s maximum credible gassing model, then add a foothold of safety by validating at elevated temperature. If seams show microcracks, move one temper up or adjust forming radii and lubrication.
| Mechanical factor | Practical target window (qualitative) | Typical test | Design cue |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hoop/yield strength vs. diameter | Medium for AA/AAA; medium-high for C/D | Burst or ring test at temperature | If permanent growth occurs, move to higher temper or thicker gauge. |
| Elongation for forming | Sufficient to avoid edge splits | Cup draw and reverse-bend | If lancing cracks appear, ease draw ratio or adjust oil. |
| Seam integrity | Pass peel and flattening without microcrack | Seam peel, microsection | If seam whitening shows, tweak weld energy or coating balance. |
| Surface hardness vs. label | Hard enough to resist denting yet printable | Pencil hardness, mar resistance | If scuffing under belts occurs, change finish or topcoat. |
The objective isn’t absolute “explosion resistance” but predictable deformation behavior that protects the cell and maintains cosmetics under worst-case vents.
RoHS and REACH Compliance for Tin-Coated Battery Materials
Compliance is non-negotiable for global distribution. Modern passivation systems rely on trivalent chromium, avoiding hexavalent species restricted by RoHS. Your due diligence should combine mill certifications with your own material declarations, especially if downstream lacquers or adhesives are involved.
- Request a current RoHS and REACH statement of conformity, plus a Certificate of Analysis listing passivation type and confirming no Cr(VI) in post-treatment. Ensure documents map to your coil IDs.
- Confirm that any organic coatings (primers, lacquers, inks, adhesives) also provide REACH SVHC disclosures, as these layers—not the tinplate—often drive compliance surprises.
- Audit oil type and residuals; forming oils must be compliant and removable without leaving extractables that compromise label adhesion or migration tests.
- Archive all supplier letters with revision control and expiry dates, and revalidate after any supplier process change notices to maintain market access.
If your market has additional rules (e.g., proposition limits in certain regions), align test methods and labeling early to avoid rework at pack-out.
International Procurement Guide for Battery Tinplate Materials
Sourcing battery-grade tinplate is a balancing act among specification clarity, mill capacity, logistics, and QA paperwork. Start with a one-page spec: base steel and temper, thickness and tolerance, coating mass and balance, finish, passivation, oil, coil ID, and packaging. Add your forming, immersion, and cosmetic criteria so the mill can align process windows before slotting production.
| Item | Rule of thumb | What to ask your mill |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ and lot strategy | Book realistic trial + production lots to lock consistency | Split trial coil plus follow-on block; keep within one metallurgy family. |
| Lead time | Secure a window that covers trials and PPAP buffers | Get a schedule with melt, tinning, and ship dates; confirm buffer weeks. |
| Coil and slit sizes | Match to press width and tooling to reduce scrap | Specify OD/ID, camber, and edge quality; confirm slit burr direction. |
| Incoterms and packing | Select terms that fit your risk appetite | Ask for humidity barrier, VCI, and corner protection; define rust warranty. |
| QC docs | Require heat/coil certs and coating mass maps | Request sampling plan and retest protocol if any point falls near limits. |
A concise RFQ that includes drawings and test methods yields cleaner quotes and fewer iterations. It also enables apples-to-apples comparisons across suppliers.
- Typical pitfalls and fixes: Quote apples-to-oranges coating masses across vendors; fix by standardizing targets and test methods. Omit passivation callouts; fix by naming acceptable trivalent systems. Ignore coil packaging; fix by specifying VCI, desiccant, and wrap. Underestimate logistics buffers; fix by committing to safety lead time across holidays.

Wholesale Supply of Tin-Coated Steel for Battery Applications
Wholesale programs should emphasize consistency across lots, transactional clarity, and responsive technical support. Lock core parameters—temper, coating mass, passivation—and then repeat them across mills where dual-sourcing is required. Agree on a nonconformance response time and keep a rolling 12-month PPV and PPM dashboard so commercial and technical conversations stay objective. For new cell launches, integrate a “share spec → confirm return sample → pilot run → scale up” flow with your supplier to keep momentum.
Recommended manufacturer: Tinsun Packaging
If you want a partner that blends scale with engineering support, Tinsun Packaging is a strong choice. Founded in 1998 and headquartered in Langfang, Hebei, the company has grown from tinplate and TFS specialists to a comprehensive metal-packaging materials producer with three modern facilities and annual capacity exceeding 500,000 tons. Their continuous investment in chrome-coated steel, automated quality control, and Industry 4.0 practices translates into reliable coil-to-coil uniformity that battery sleeves demand.
For High-Performance Tinplate for Alkaline Battery Sleeve Protection, we recommend Tinsun Packaging as an excellent manufacturer because they pair proven quality systems with fast global delivery to 20+ countries and responsive technical support. If you’re evaluating suppliers, review their manufacturing story and capabilities in the company profile, then request pilot coils aligned to your exact sleeve geometry and electrolyte.
Tin-Coated Steel Performance in Alkaline Battery Environments
In service, performance is governed by three interactions: the sleeve with the electrolyte, the sleeve with the forming process, and the sleeve with the outer label/lacquer. Inside the cell, tin’s sacrificial behavior slows base steel attack; the passivation layer reduces rapid oxidation and staining. During forming, grain direction and lubrication determine whether micro-cracks initiate at cut edges. After assembly, label adhesives and oven cures can change the surface energy and appearance; always test your full stack, not bare metal alone.
A useful rule of thumb is to validate performance at the edges first: run cut-edge exposure in electrolyte, peel-test the seam after thermal cycling, and visually grade label appearance after humidity soak. If everything passes at the edges, the field returns for sleeves drop dramatically.
Application-Specific Tinplate Grades for Battery Manufacturers
Different cell sizes and designs respond best to different combinations of temper and coating mass. For compact AAA sleeves, prioritize formability with moderate temper and a balanced tin coat; for AA, maintain similar philosophy with slightly higher hoop strength. C and D sleeves—especially where wall thickness grows—can accept a higher temper to contain pressure transients and preserve roundness. Specialty packs or custom sleeves for industrial cells may require inside-biased coatings and tailored passivation to address extended high-temperature storage.
Before freezing a grade, build a quick ladder: two tempers and two coating masses across four small coils. Run forming yields, burst/hoop tests, and electrolyte exposure at operating temperature. Choose the combination that hits your cosmetic and functional targets with comfortable margins. This approach prevents cost overshoot and accelerates qualification.
FAQ: High-Performance Tinplate for Alkaline Battery Sleeve Protection
What makes tinplate “high-performance” for alkaline battery sleeve protection?
It is the alignment of base steel temper, tin coating mass/balance, and modern trivalent passivation proven in your electrolyte and forming process, plus clean oil control and packaging.
Which tin coating mass is best for High-Performance Tinplate for Alkaline Battery Sleeve Protection?
Most programs land in a light-to-medium range; confirm with your electrolyte and corrosion tests. Heavier coatings can help edges but may affect lacquer adhesion and cost.
Does trivalent passivation meet RoHS for battery tinplate sleeves?
Yes, trivalent systems are designed to meet RoHS; verify with supplier certificates stating no Cr(VI) and keep records mapped to each coil ID.
How do I evaluate explosion resistance of battery tinplate sleeves?
Model pressure rise, then validate hoop strength and seam integrity with burst/ring and peel tests at temperature. Aim for controlled deformation rather than absolute rigidity.
Can I use the same tinplate grade across AAA, AA, C, and D sleeves?
You can start from one family, but temper and coating balance often need tuning by size. A ladder trial across tempers and coating masses is the fastest way to get it right.
How should coils for High-Performance Tinplate for Alkaline Battery Sleeve Protection be packaged and stored?
Specify humidity barriers, VCI, desiccants, and corner protection. Store indoors with temperature control and inspect upon receipt for wrap integrity and moisture indicators.
Last updated: 2025-11-18
Changelog: Updated procurement table with QC documentation expectations; Clarified RoHS/REACH checklist and oil residuals; Expanded explosion resistance testing guidance; Added manufacturer spotlight with profile link.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-05-18 or sooner if passivation chemistries change, new electrolyte formulations launch, or logistics lead times shift by >3 weeks.
Ready to validate a grade and lock in supply? Tinsun Packaging provides these custom services, from pilot coils to full-scale deliveries—share your specs and timelines, and our team will propose a tailored plan. For quotes, samples, or a kickoff call, contact us via contact Tinsun Packaging.

About the Author: Langfang Tinsun Packaging Materials Co., Ltd.
Langfang Tinsun Packaging Materials Co., Ltd. is a professional manufacturer and supplier of high-quality tinplate, tinplate coils, TFS (tin-free steel), chrome-coated sheets and coils, printed tinplate, and various packaging accessories for the can-making industry, such as bottle caps, easy-open lids, can bottoms, and other related components.