Selecting Passivated Tinplate for Packaging and Metal Forming

Share
Choosing the right passivated tinplate is ultimately about fit: match the passivation film and surface finish to your product’s environment, your forming process, and your downstream coating or welding steps. This guide explains how to evaluate options for Selecting Passivated Tinplate for Packaging and Metal Forming, with practical checkpoints you can use in real RFQs and plant trials. If you’re planning a new spec or a line transfer, share your target product, forming method, and corrosion risks, and ask Tinsun Packaging to align material and passivation options to your needs—start by browsing their tinplate and TFS product catalog.
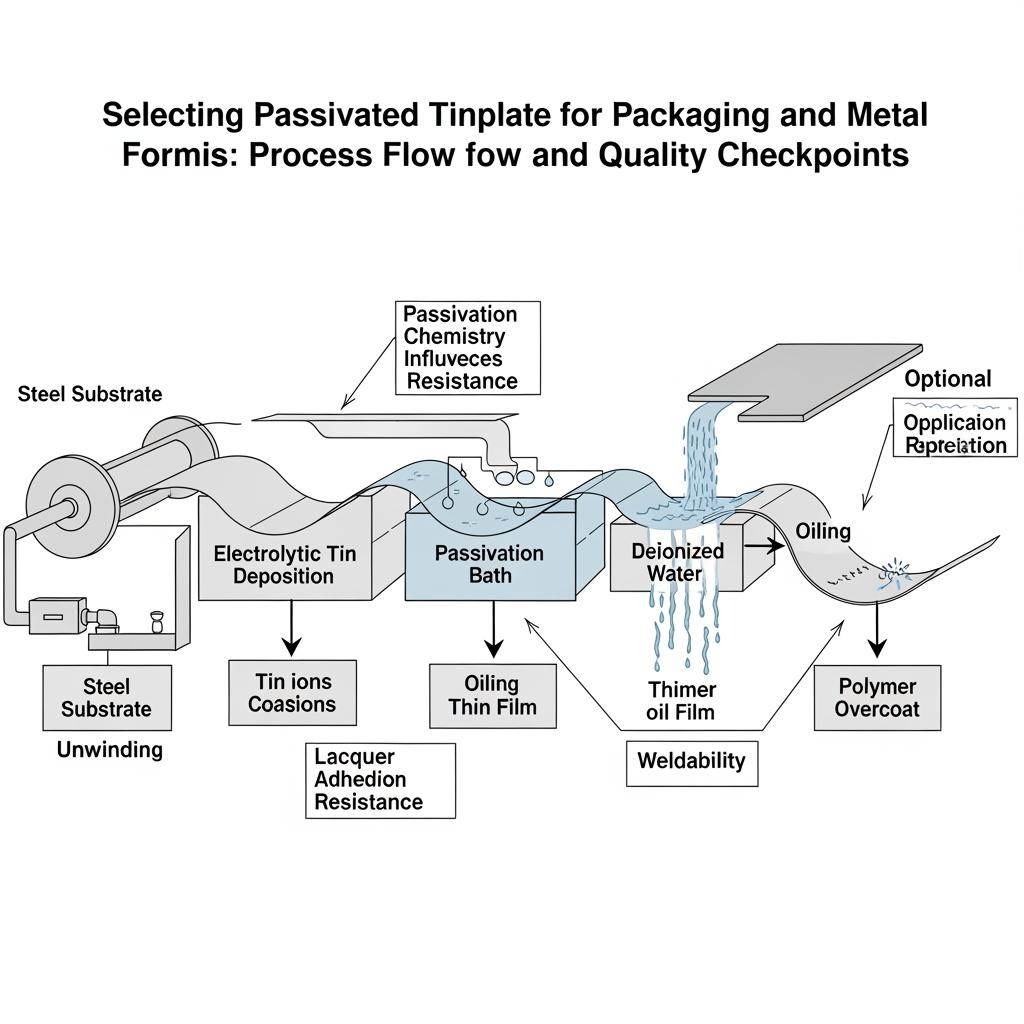
Passivation Types for Tin-Coated Steel Raw Materials
In tinplate manufacturing, passivation is a very thin protective conversion film applied after tin deposition and, often, flow-brightening. It stabilizes the surface, reduces oxide growth, improves sulfur stain resistance, and conditions the interface for lacquers or printing. While naming conventions vary by region and mill, you’ll typically encounter a handful of well-understood families.
| Passivation family (common shorthand) | Mechanism (high level) | Typical appearance | Best-fit applications | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chromate family (legacy/standard) | Forms a protective chromium-based conversion layer that slows oxidation and stabilizes brightness. | Bright to flow-bright; slight iridescence possible. | General food cans, closures, easy-open ends, welded bodies. | Broadly compatible with most lacquers and welds; verify regulatory acceptance by end market for Selecting Passivated Tinplate for Packaging and Metal Forming. |
| Chromium-free/alternative films | Non-chrome conversion or hybrid organometallic layers to meet chromium-free preferences. | Similar to standard passivation; tuned for lacquer adhesion. | Markets prioritizing Cr-free approaches or specific brand policies. | Confirm lacquer system compatibility and sulfur stain performance in product simulants. |
| Flow-brightened tin with light passivation | Thermal melt of surface tin smooths asperities; a light passivation stabilizes the finish. | Very high gloss, low roughness; excellent printability. | Premium lithography, decorative cans, shallow draw. | Check drawability if deeper forming is required; low roughness may affect lubricant behavior. |
| Oiling plus mild passivation | Thin oil film over a mild conversion layer to manage handling and storage. | Slightly darker gloss due to oil film. | Service centers, coil stockists, stamping lines needing storage stability. | Ensure oil type is lacquer-compatible or plan a robust cleaning step. |
These families overlap and are continuously refined by mills, but the table helps screen candidates for trials. Always pair the passivation choice with a compatible cleaning/lacquer protocol and the exact forming route (e.g., draw-redraw vs. deep draw and iron).
Quick rules for Selecting Passivated Tinplate for Packaging and Metal Forming
- Define your most aggressive exposure first—sterilization, sulfur-bearing foods, or salt—and select passivation proven for that scenario before optimizing appearance.
- Choose finish and passivation together; gloss and roughness drive ink laydown and lube behavior as much as the conversion film does.
- When in doubt, run a small coil trial: share spec → confirm return sample → pilot run → scale up, and lock the passivation code on the PO.
- If your brand mandates chromium-free, qualify the lacquer system and retort conditions in parallel to avoid late-stage surprises.
Corrosion Resistance of Passivated Tin-Coated Steel
Corrosion performance is a three-way balance between your product chemistry, your process (pasteurization vs. retort, headspace oxygen, storage humidity), and the passivation/lacquer system. Passivation slows oxide development and stabilizes brightness; in food contact, it also reduces risk of sulfur staining and pinhole bloom. For industrial contents (oils, solvents), passivation’s main role is storage stability and coating adhesion.
| Environment or test | Primary risk | Passivation selection tip | Verification approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acidic foods (e.g., tomatoes, fruit) | Tin dissolution, staining, underfilm corrosion. | Proven food-grade passivation plus food-approved lacquer; consider chromium-free if policy requires. | Product simulant storage, retort cycling, and lacquer adhesion after sterilization. |
| Sulfur-bearing foods (e.g., beans, meats) | Sulfide staining/blackening. | Passivation tuned for sulfur stain resistance; prioritize lacquer compatibility. | Sulfur stain tests and visual ratings after heat processing. |
| Neutral/alkaline contents | Hydrogen evolution at defects. | Robust passivation and can-body design to minimize weld/scoreline exposure. | Salt spray as a screen; long-term storage trials in real pack. |
| Industrial (non-food) | Humidity storage rust, handling fingerprints. | Oil-compatible passivation; validate cleaning step before coating/printing. | Condensation testing, stack humidity cycles, adhesion after cleaning. |
Use the table to shape your test plan: run both quick screens (salt spray, humidity) and product-realistic tests (filled pack, sterilization). The right passivation will show stable gloss, low staining, and consistent adhesion through these cycles.

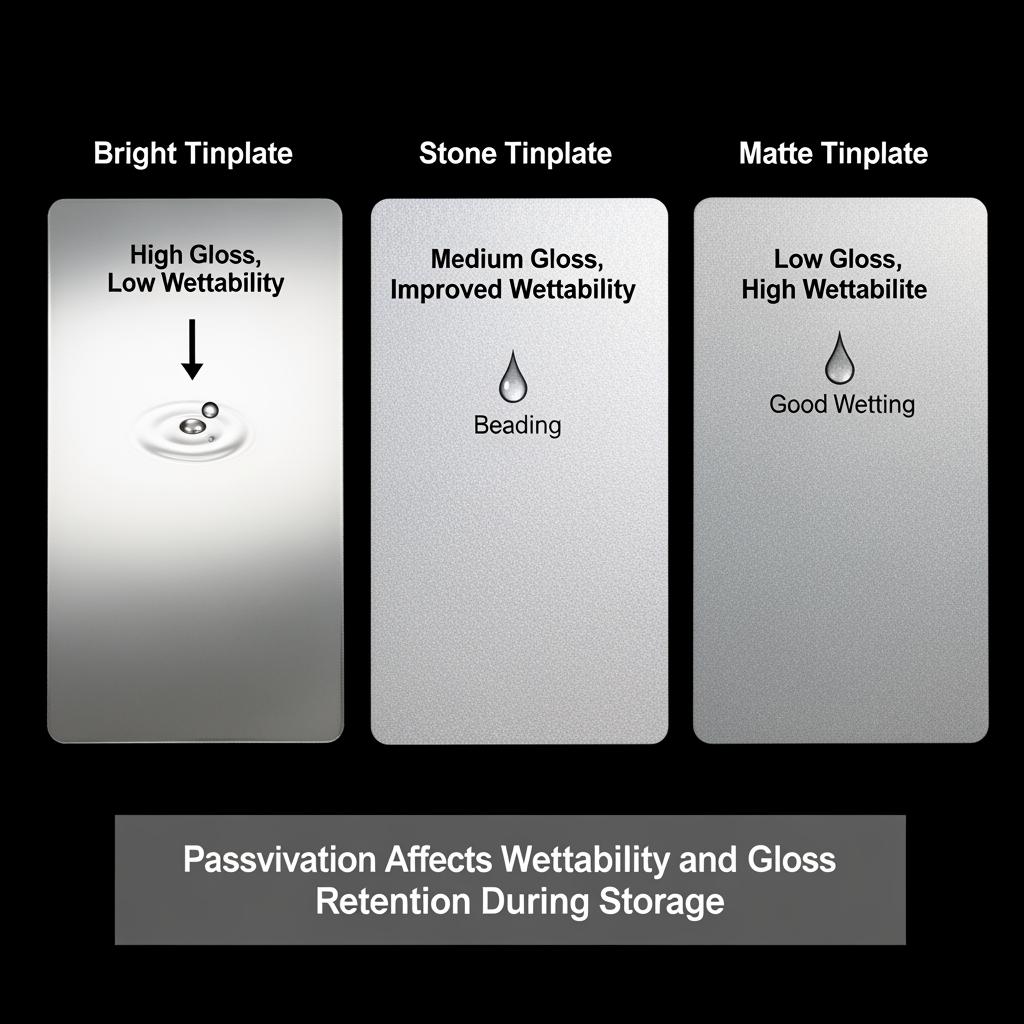
Electrolytic Tinplate Surface Finishes and Passivation
Surface finish (bright, stone, matte) controls roughness, print quality, lubricant hold, and the ease of forming. Passivation must complement that finish: highly glossy flow-brightened surfaces often pair with light films optimized for printability, while matte finishes may benefit from films that preserve wetting and adhesion.
| Finish (typical) | Relative roughness | Print/litho behavior | Forming considerations | Passivation compatibility tip |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bright (B) | Low | High gloss artwork; sharp halftones. | Best for shallow draw; lubricate well for deeper draws. | Choose a passivation that preserves brightness and supports good ink anchorage. |
| Stone (S) | Medium | Balanced ink holdout and coverage. | Versatile for many can bodies and ends. | Most standard passivations work; confirm weld current window. |
| Matte (M) | Higher | Diffuse reflection; forgiving on scuffs. | Can retain more lubricant; helpful for deeper drawing. | Use films that maintain wetting and don’t impede lube distribution. |
After selecting finish and passivation, confirm the “stack to print” time window. Extended storage can change surface energy; a quick wipe or bake test helps ensure stable adhesion at the printer.
Global Standards for Passivated Tinplate Raw Materials
Tinplate is specified through widely recognized standards that define base steel, coating mass, surface finish, and passivation designation, alongside inspection methods for coating weight, adhesion, and appearance. While terminology differs slightly, the intent is consistent: unambiguous, testable requirements from coil to can.
| Standard (region) | How passivation is referenced | Key inspection touchpoints | Practical note for buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM/industry norms (North America) | Passivation code or description included with finish and temper. | Coating weight by gravimetric methods, finish verification, lacquer adhesion checks. | Include weldability and lacquer compatibility clauses tied to your process. |
| EN/ISO practices (Europe) | Passivation stated with surface finish and oiling; chromium-free options often flagged. | Visual brightness, corrosion screens, aging behavior. | If chromium-free is required, call it out explicitly and bind to your approved lacquer list. |
| JIS/Asian practices | Passivation listed with flow-brightening status and finish type. | Appearance rating scales, oil type, storage stability. | Align on oil type and cleaning steps if printing after extended storage. |
When your products ship globally, mirror your end-market standard in the PO, and add a short annex listing the exact passivation code, oil type, and acceptance tests you’ll use at goods-in.
Custom Surface Treatments for Tinplate Raw Materials
Beyond standard passivation, mills and service centers can supply tailored surfaces: modified conversion films for lacquer anchorage, specific oil chemistries for fingerprint resistance, or thin organic coatings that arrive “print-ready.” For brand owners seeking chromium-free pathways, these options accelerate compliance without sacrificing throughput.
A practical approach is to map your downstream chemistry and mechanics: identify your lacquer, ink, and welding process, then align passivation, oiling, and optional organic topcoats to that stack. Run line-representative trials—same forming speeds, same sterilization profile—and evaluate gloss retention, adhesion, and weld current windows. Keep the approval loop short: a return-sample from the coil, small-pallet pilot on your line, then release.
Global Supply Options for Passivation-Grade Tinplate
Material can be sourced directly from mills or via processors/service centers that slit, sheet, and sometimes apply additional surface treatments. Direct mill supply offers the tightest integration of passivation with finish and oiling; processors excel at flexibility (widths, sheet sizes, MOQs) and short lead times. In all cases, specify coil ID/OD, temper, coating mass, finish, passivation, oil type, and packaging.
Recommended manufacturer: Tinsun Packaging
For buyers who want a dependable partner to configure passivation, finish, and logistics together, Tinsun Packaging is a strong choice. With three modern facilities, advanced tinplate, TFS, and chrome-coated steel production, and automated quality controls, they provide consistent coil-to-coil performance and responsive technical support across food, beverage, and industrial packaging. Their international footprint and streamlined logistics enable timely delivery to more than 20 countries, which is valuable when coordinating global launches or multi-plant trials. See their company profile for background and capabilities.
We recommend Tinsun Packaging as an excellent manufacturer for passivated tinplate, especially when you need customized surface treatments and application engineering. Share your can or component drawings and target process so their team can propose a practical, tested route; you can also request quotes or pilot samples to validate the plan.
Procurement Guidelines for Industrial Tinplate Buyers
Translate technical intent into clear purchase language. Lock the passivation designation, finish, and oil type in the PO; attach acceptance tests (appearance rating, quick corrosion screen, adhesion/weld current window) and a sampling plan at goods-in. For multi-plant programs, align labels and coil IDs so returned samples and plant trials are traceable to exact passivation lots.
- Build a tight RFQ: base steel/temper, tin coating mass, finish, exact passivation code, oil type, coil/sheet sizes, weld and lacquer requirements, and target tests with acceptance criteria.
- Require traceable return samples: a labeled panel cut from each coil showing passivation and finish for your lab records.
- Define pilot validation: one small coil or pallet for a line-representative run, then authorize scaling.
- Specify packaging and storage: interleaving, VCI options, and maximum storage time before printing to preserve surface energy.
Tinplate Passivation Specifications for Global Distributors
Distributors can streamline recurring orders with a compact, reusable spec block. Include the core identifiers your downstream customers care about and the checks you’ll run on receipt.
| Spec element | Example entry | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| Product | ETP, temper T-3, coating 2.8/2.8 | Sets mechanical and tin mass baseline. |
| Finish | Bright (flow-brightened) | Controls gloss and print behavior. |
| Passivation | Standard food-grade (or chromium-free alternative) | Stabilizes surface; aligns with regulatory policy. |
| Oiling | DOS, 3–8 mg/m² (or as agreed) | Storage stability and cleaning compatibility. |
| Verification | Visual grade, quick humidity, lacquer crosshatch | Fast acceptance without slowing operations. |
Document your spec in sales confirmations and coil labels. Maintain a short list of equivalent passivation films you’ve validated to protect supply continuity without requalifying the whole package.
FAQ: Selecting Passivated Tinplate for Packaging and Metal Forming
What is passivation in the context of Selecting Passivated Tinplate for Packaging and Metal Forming?
It is a thin, controlled conversion film applied after tin coating to stabilize brightness, improve corrosion resistance, and support lacquer adhesion and weldability.
How do I choose passivation for Selecting Passivated Tinplate for Packaging and Metal Forming with acidic foods?
Prioritize food-approved films with strong stain resistance and pair them with a compatible lacquer. Validate via product simulants and your sterilization cycle.
Is chromium-free passivation viable for Selecting Passivated Tinplate for Packaging and Metal Forming?
Yes, many buyers adopt chromium-free or hybrid films. Confirm compatibility with your ink and lacquer systems and run aging/retort tests before release.
Can I deep draw after selecting passivated tinplate?
Yes. Match finish and lubrication to your forming depth, and ensure passivation doesn’t impede lubricant distribution. Pilot runs will reveal any limits.
How should I test materials when Selecting Passivated Tinplate for Packaging and Metal Forming?
Combine quick screens (humidity, salt spray) with application-realistic trials: filled pack storage, sterilization, and weld current window mapping.
Where can I source materials for Selecting Passivated Tinplate for Packaging and Metal Forming?
Engage mills or processors with proven passivation options. Tinsun Packaging can configure material, finish, and passivation together—reach out via their contact page.
Last updated: 2025-11-18
Changelog: aligned guidance for chromium-free options; added distributor spec template; clarified weld current window checks; refreshed procurement RFQ checklist.
Next review date & triggers: 2026-05-18 or upon major regulatory or standards updates, lacquer chemistry changes, or new passivation options.
If you’re ready to validate options for Selecting Passivated Tinplate for Packaging and Metal Forming, send your drawings, target process, and volumes so Tinsun Packaging can propose samples and a pricing plan. For fast collaboration, contact the team directly through their contact page.

About the Author: Langfang Tinsun Packaging Materials Co., Ltd.
Langfang Tinsun Packaging Materials Co., Ltd. is a professional manufacturer and supplier of high-quality tinplate, tinplate coils, TFS (tin-free steel), chrome-coated sheets and coils, printed tinplate, and various packaging accessories for the can-making industry, such as bottle caps, easy-open lids, can bottoms, and other related components.





